Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2012; 18(36): 5042-5050
Published online Sep 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i36.5042
Published online Sep 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i36.5042
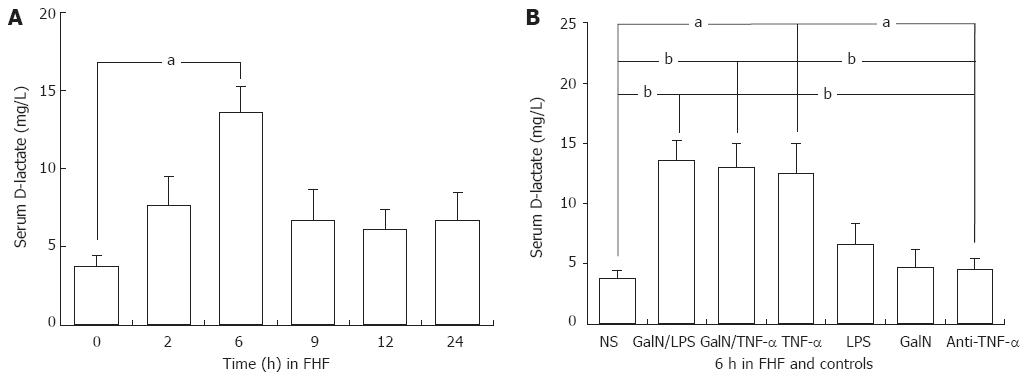
Figure 1 Systemic blood D(-)-lactate levels in the mouse model of fulminant hepatic failure and controls.
Systemic blood D (-)-lactate levels 2, 6, 9, 12 and 24 h after injection in D-galactosamine (GalN)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated mice, and 6 h after injection in the saline, GalN, LPS, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), anti-TNF-α immunoglobulin G antibody-pretreated groups. n = 5 rats for each time point. NS: Normal saline; FHF: Fulminant hepatic failure. The level of significance was set at aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs baseline (NS group). Data are reported as the mean ± SD.
- Citation: Li GZ, Wang ZH, Cui W, Fu JL, Wang YR, Liu P. Tumor necrosis factor alpha increases intestinal permeability in mice with fulminant hepatic failure. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(36): 5042-5050
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i36/5042.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i36.5042