Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2012; 18(35): 4967-4972
Published online Sep 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i35.4967
Published online Sep 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i35.4967
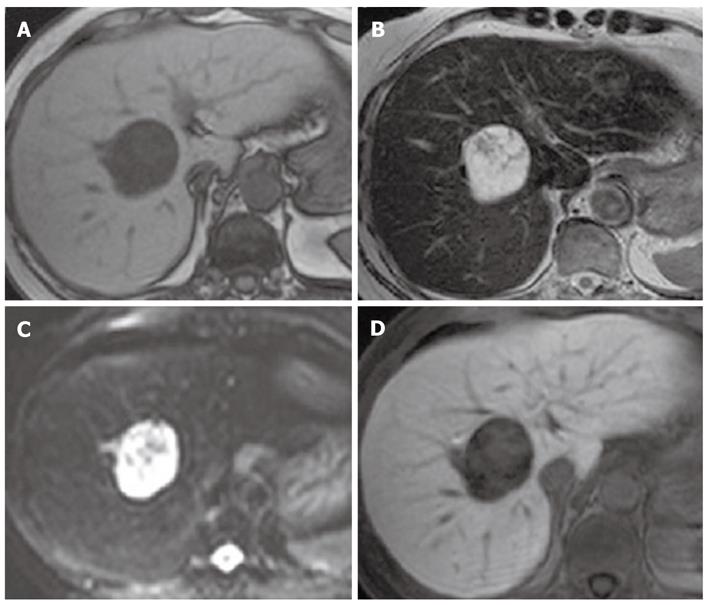
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging.
A: T1-weighted imaging; B: T2-weighted imaging; C: Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI); D: Hepatobiliary phase. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a hypointense mass on T1-weighted imaging, and a mixed hypo- and hyperintense mass on T2-weighted imaging and on DWI. Gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine penta-acetic acid-enhanced MRI showed a defect in the hepatobiliary phase.
- Citation: Ota Y, Aso K, Watanabe K, Einama T, Imai K, Karasaki H, Sudo R, Tamaki Y, Okada M, Tokusashi Y, Kono T, Miyokawa N, Haneda M, Taniguchi M, Furukawa H. Hepatic schwannoma: Imaging findings on CT, MRI and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(35): 4967-4972
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i35/4967.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i35.4967