Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2012; 18(34): 4704-4713
Published online Sep 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4704
Published online Sep 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4704
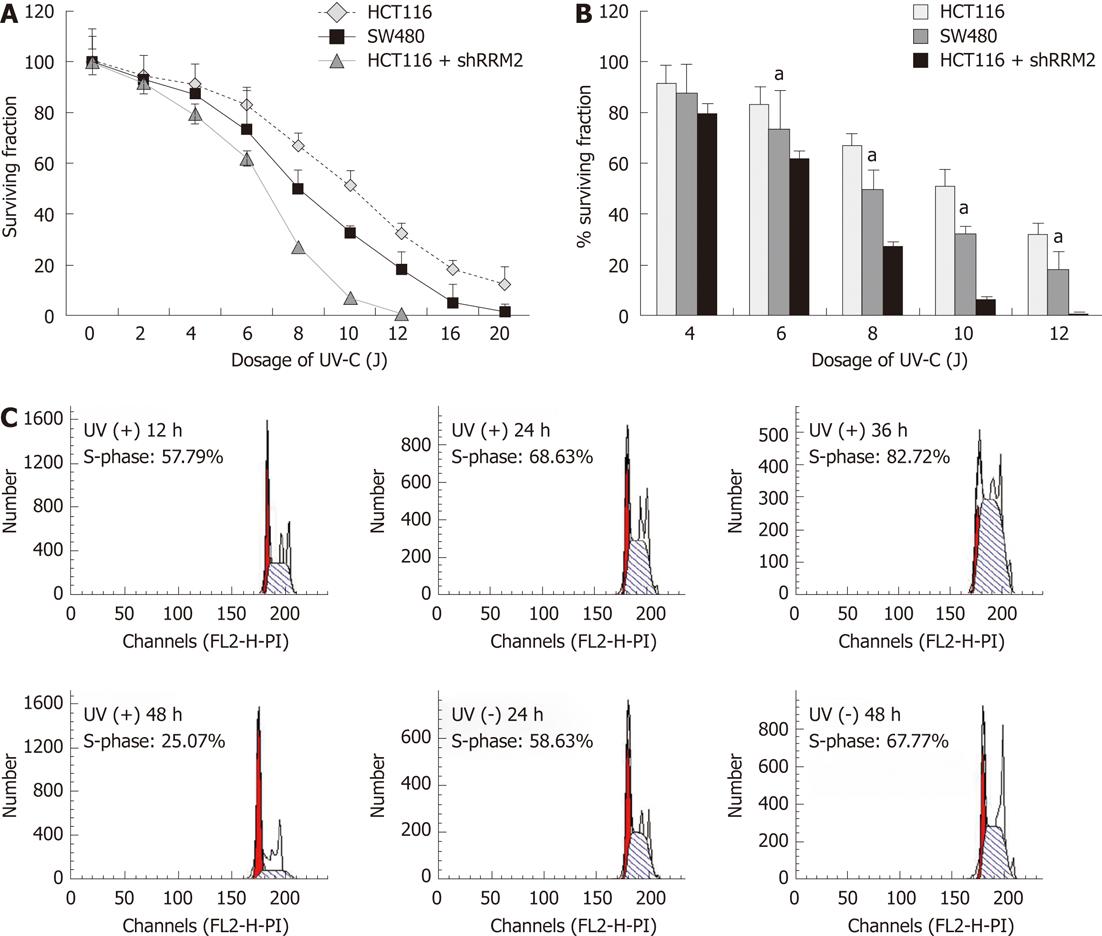
Figure 4 Inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase M2 by expression of antisense hRRM2 results in increased ultraviolet sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells.
A: Ribonucleotide reductase M2 (RRM2)-/- tumors and RRM2-depleted cells are hypersensitive to ultraviolet (UV)-C. SW620 cells, HCT116 cells (WT), and HCT116 cells (RRM2-/-) were irradiated with increasing doses of UV-C and assayed for colony formation; B: Bar graph showing the quantification of the surviving fraction following 4-12 J irradiation. HCT116 cells transfected with shRRM2 revealed significant RRM2 depletion, and its colony-forming ability under UV radiation was suppressed, aP < 0.05 vs HCT116 group; C: Effects of colorectal cancer cell cycle irradiated with UV-C. After UV irradiation, an S-phase increase could be seen, starting from 12 h with a continued significant increase at 24 and 36 h.
- Citation: Lu AG, Feng H, Wang PXZ, Han DP, Chen XH, Zheng MH. Emerging roles of the ribonucleotide reductase M2 in colorectal cancer and ultraviolet-induced DNA damage repair. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(34): 4704-4713
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i34/4704.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4704