Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2012; 18(33): 4618-4626
Published online Sep 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i33.4618
Published online Sep 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i33.4618
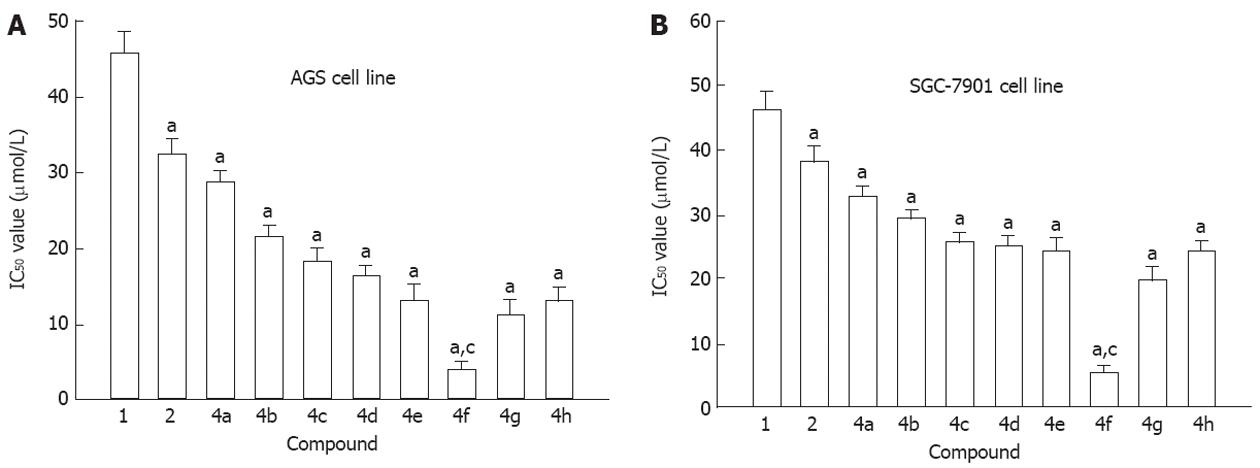
Figure 1 Inhibition of cell viability by genistein and genistein analogues.
A: AGS cell line; B: SGC-7901 cell line. aP < 0.05 vs treatment with genistein; cP < 0.05 vs treatment with genistein or other genistein analogues. 1: Genistein (5,7,4'-trihydroxylisoflavone); 2: 7-difluoromethyl genistein; 4a: 7-difluoromethyl-5,4'-dimethyl genistein; 4b: 7-difluoromethyl-5,4'-diethyl genistein; 4c: 7-difluoromethyl-5,4’-di-n-propyl genistein; 4d: 7-difluoromethyl-5,4’-di-benzyl genistein; 4e: 7-difluoromethyl-5,4'-diheptyl genistein; 4f: 7-difluoromethyl-5,4'-di-n-octyl genistein; 4g: 7-difluoromethyl-5,4'-didecyl genistein; 4h: 7-difluoromethyl-5,4'-diisobutyl genistein.
- Citation: Xiang HL, Liu F, Quan MF, Cao JG, Lv Y. 7-difluoromethoxyl-5,4’-di-n-octylgenistein inhibits growth of gastric cancer cells through downregulating forkhead box M1. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(33): 4618-4626
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i33/4618.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i33.4618