Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2012; 18(33): 4570-4577
Published online Sep 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i33.4570
Published online Sep 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i33.4570
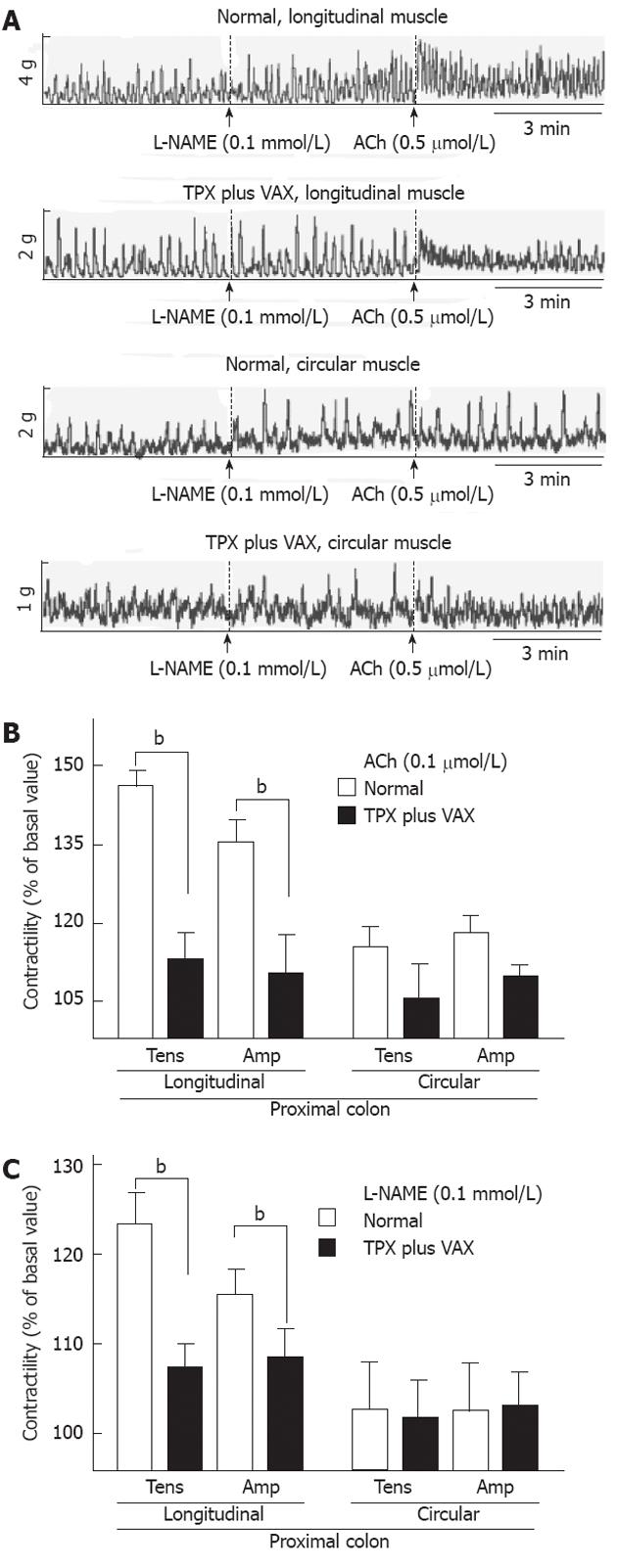
Figure 6 Reduced contractile activity of the proximal colonic muscles in the thyroparatyroidectomy plus subdiaphragmatic vagotomy rats.
Animals were sacrificed at 8 d after subdiaphragmatic vagotomy (VAX), and intact proximal colonic strips prepared from the age-matched normal and thyroparatyroidectomy (TPX) plus VAX rats were longitudinally or circularly mounted in a 10 mL organ bath. The contractile responses of colonic strips to acetylcholine (Ach) and N-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) were measured by isometric force transducers. Figures show the representative tracings (A) and contractile responses to ACh (B) and L-NAME (C). Each point represents the mean ± SE of 7-9 rats. bP < 0.01 vs normal and sham-operated groups.
- Citation: Lee JH, Kwon OD, Ahn SH, Choi KH, Park JH, Lee S, Choi BK, Jung KY. Reduction of gastrointestinal motility by unilateral thyroparathyroidectomy plus subdiaphragmatic vagotomy in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(33): 4570-4577
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i33/4570.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i33.4570