Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2012; 18(31): 4102-4117
Published online Aug 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4102
Published online Aug 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4102
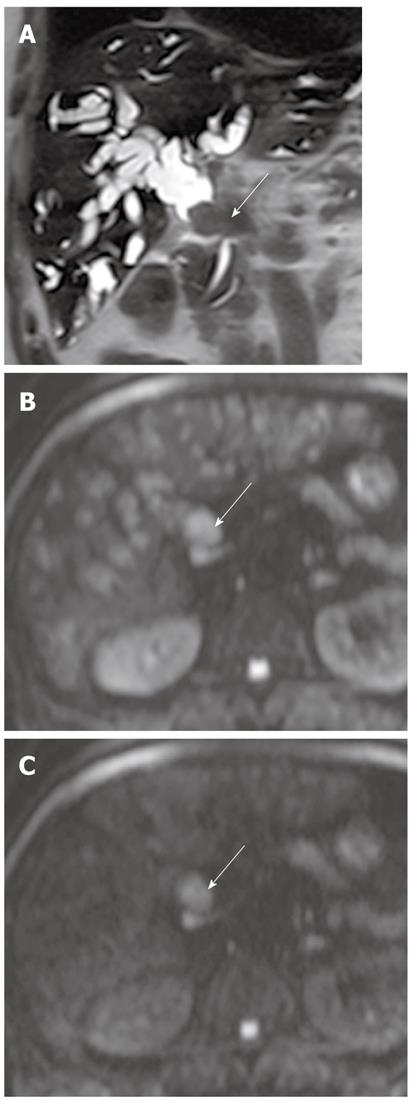
Figure 15 Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in a 62-year-old man.
A: Coronal T2-weighted rapid acquisition relaxation enhancement image shows a mass (arrow) in the distal common bile duct and marked upstream bile duct dilatation; B: DWI at b = 800 s/mm2 shows a mass with high signal intensity (arrow), but the signal intensity of bile is also increased; C: DWI at b = 1000 s/mm2 shows a mass with high signal intensity (arrow). Note that the signal intensity of bile in the bile duct is significantly reduced. DWI: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.
- Citation: Lee NK, Kim S, Kim GH, Kim DU, Seo HI, Kim TU, Kang DH, Jang HJ. Diffusion-weighted imaging of biliopancreatic disorders: Correlation with conventional magnetic resonance imaging. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(31): 4102-4117
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i31/4102.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4102