Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2012; 18(30): 3977-3991
Published online Aug 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.3977
Published online Aug 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.3977
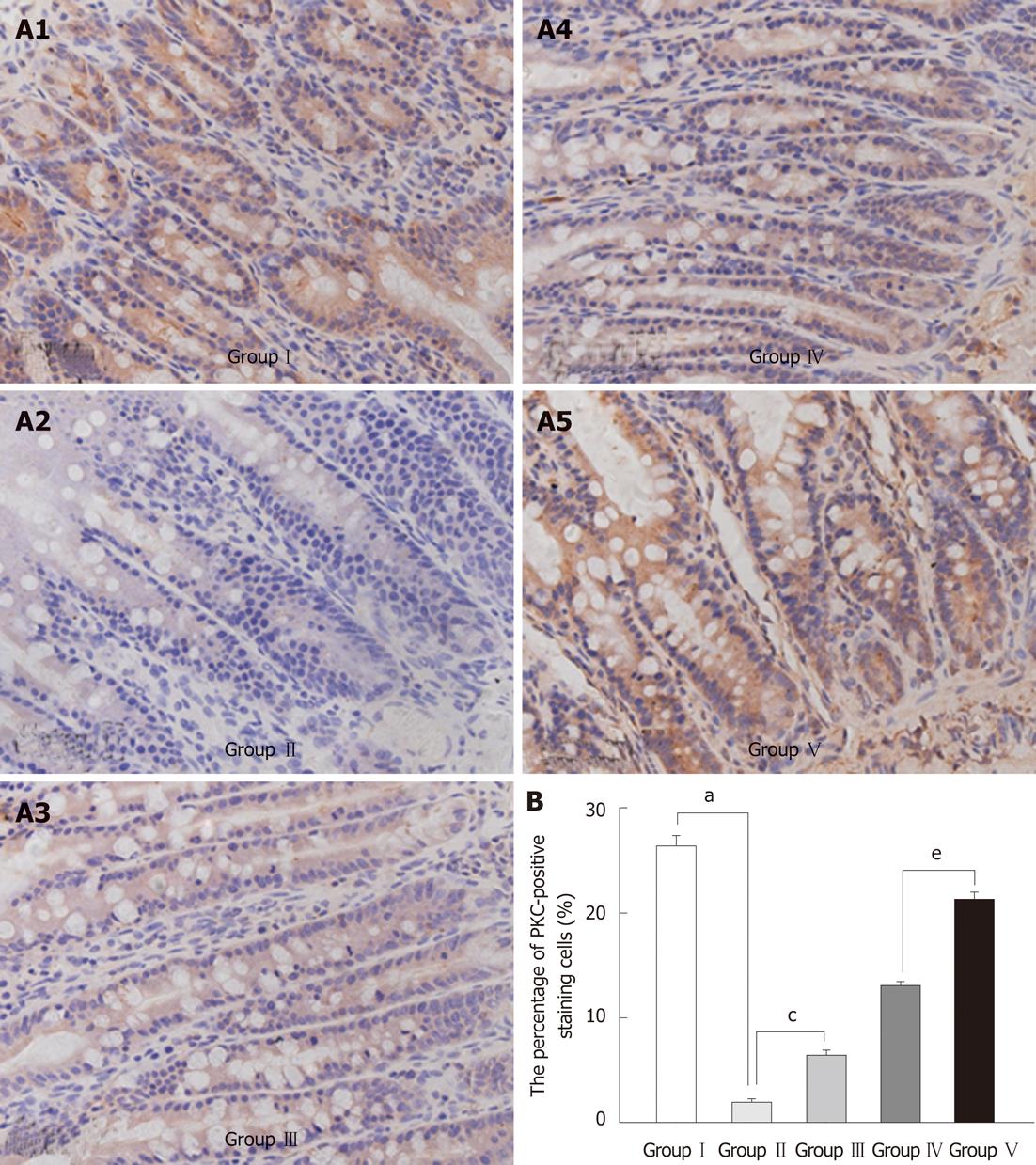
Figure 5 Effects of probiotics on the expression of protein kinase C in the mucosa of the terminal ileum.
A: Probiotics effects on biliary obstruction-induced expression of protein kinase C (PKC) as determined by immunohistochemistry. Images shown are representative of at least three regions observed on the same slide; B: Statistical evaluation of effects of addition of probiotics (Lactobacillus plantarum) on the expression of PKC in the intestinal mucosal epithelium. Data in the bar graph represent mean ± SD of the three separate experiments. aP < 0.05 Group I vs Group II; cP < 0.05Group II vs Group III; eP < 0.05 Group IV vs Group V. Group I : Sham-operation; Group II: Bile duct ligation (BDL); Group III: BDL + Lactobacillus plantarum (L. plantarum); Group IV: BDL + internal biliary drainage (IBD); Group V = BDL + IBD + L. plantarum.
-
Citation: Zhou YK, Qin HL, Zhang M, Shen TY, Chen HQ, Ma YL, Chu ZX, Zhang P, Liu ZH. Effects of
Lactobacillus plantarum on gut barrier function in experimental obstructive jaundice. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(30): 3977-3991 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i30/3977.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.3977