Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2012; 18(3): 212-224
Published online Jan 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i3.212
Published online Jan 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i3.212
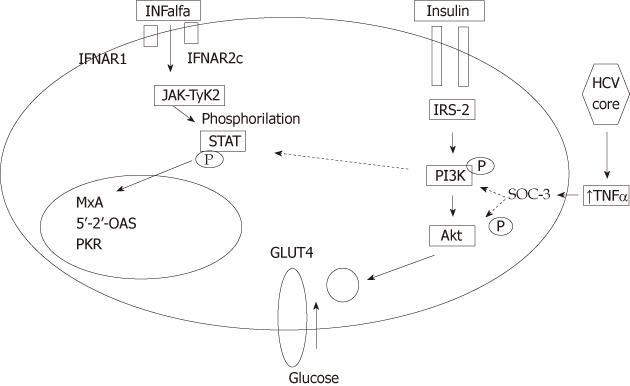
Figure 2 Interaction between hepatitis C virus core, insulin- and interferon-α signaling pathways continuous lines represent activation.
Dotted lines represent inhibition. Hepatitis C virus core protein induces expression of tumour necrosis α (TNF-α), which in turn activates suppressor of cytokines-3 (SOCS-3). Activation of SOCs-3 leads to proteasomal degradation of insulin receptor substrate and inactivates phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase (PI3K), leading to inhibition of translocation of glucose transferase (GLUT-4) to cell membrane, blocking intracellular glucose entry, with subsequent hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia and peripheral insulin resistance. Activation of SOCS-3 also leads leading to inhibition of Tyr-phosphorylation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 leading to impaired TNF-α signaling. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; IFNAR2c: Interferon receptor chain 2; IRS2: Insulin receptor substrate 2; JAK: Janus kinase; TYK2: Tyrosine kinase 2; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription.
- Citation: El-Zayadi AR, Anis M. Hepatitis C virus induced insulin resistance impairs response to anti viral therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(3): 212-224
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i3/212.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i3.212