Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2012; 18(28): 3681-3695
Published online Jul 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i28.3681
Published online Jul 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i28.3681
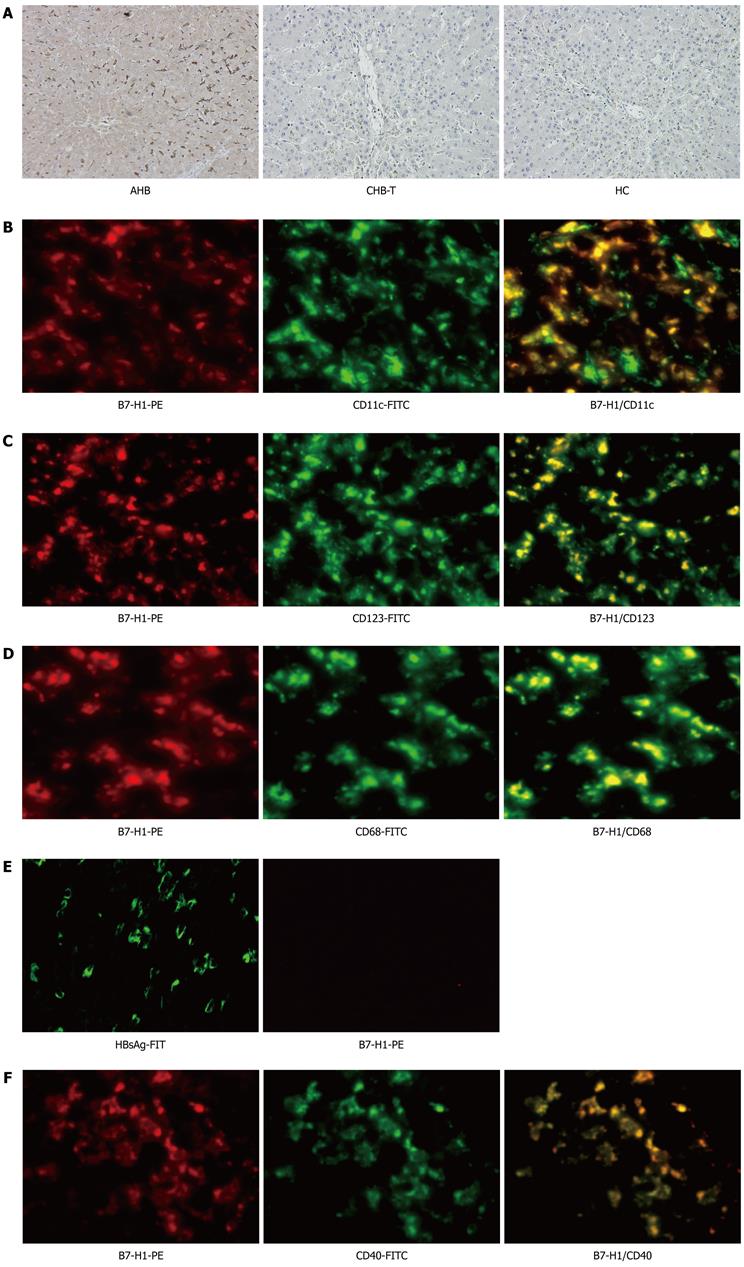
Figure 2 Analysis of intrahepatic human B7 homolog 1 expression among acute hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis B virus tolerance patients.
A: Immunohistochemical staining for intrahepatic B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1)-positive cells in acute hepatitis B (AHB), chronic hepatitis B virus tolerance (CHB-T) and healthy controls (HC). Intra-hepatic B7-H1 expression was up-regulated significantly in AHB patients, but was almost absent in both CHB-T and HC subjects. Original magnification × 200; B-D: Co-localization of B7-H1 with CD11c, CD123 and CD68 were shown by immunofluorescence double staining in liver biopsy specimens of AHB patients. B7-H1 (red) is co-localized with CD11c (green) positive mDCs (B), CD123 (green) positive pDCs (C) or CD68 (green) positive Kupffer cells (D). The 2-color merged panels were shown with co-localization visible in yellow. Original magnification × 200; E: Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and B7-H1 expression was detected by immunofluorescence stain in the liver tissue of CHB-T patients. Original magnification × 200; F: Colocalization of B7-H1 with CD40 is showed by immunofluorescence double staining in liver biopsy specimens of AHB patients. B7-H1 (red) is colocalized with CD40 (green). The 2-color merged panels were shown with colocalization visible in yellow. Original magnification × 200. PE: Phycoerythrin; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate.
- Citation: Zhang WJ, Xie HY, Duan X, Wan YL, Peng CH, Shi SH, Su R, Zheng ZH, Pan LL, Zhou L, Zheng SS. Study of human B7 homolog 1 expression in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(28): 3681-3695
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i28/3681.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i28.3681