Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2012; 18(28): 3681-3695
Published online Jul 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i28.3681
Published online Jul 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i28.3681
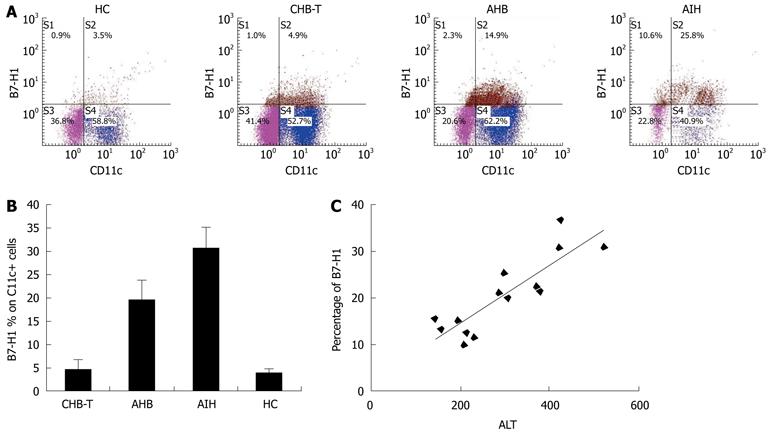
Figure 1 Circulating human B7 homolog 1 expression comparison among acute hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis B virus tolerance and autoimmune hepatitis patients.
A: Representative dot plots of double measurements of fifteen independent experiments; B: B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1) expression level on circulating myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) of acute hepatitis B (AHB) patients was significantly higher than that in chronic hepatitis B virus tolerance (CHB-T) patients (n = 12, P < 0.05). Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) patients exhibited the highest levels of B7-H1 expression on circulating mDCs among these groups (n = 3, P < 0.05); C: In AHB patients, there was significant, positive correlation between B7-H1 expression on mDCs and serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels in AHB patients (r = 0.809). HC: Healthy controls.
- Citation: Zhang WJ, Xie HY, Duan X, Wan YL, Peng CH, Shi SH, Su R, Zheng ZH, Pan LL, Zhou L, Zheng SS. Study of human B7 homolog 1 expression in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(28): 3681-3695
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i28/3681.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i28.3681