Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2012; 18(28): 3673-3680
Published online Jul 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i28.3673
Published online Jul 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i28.3673
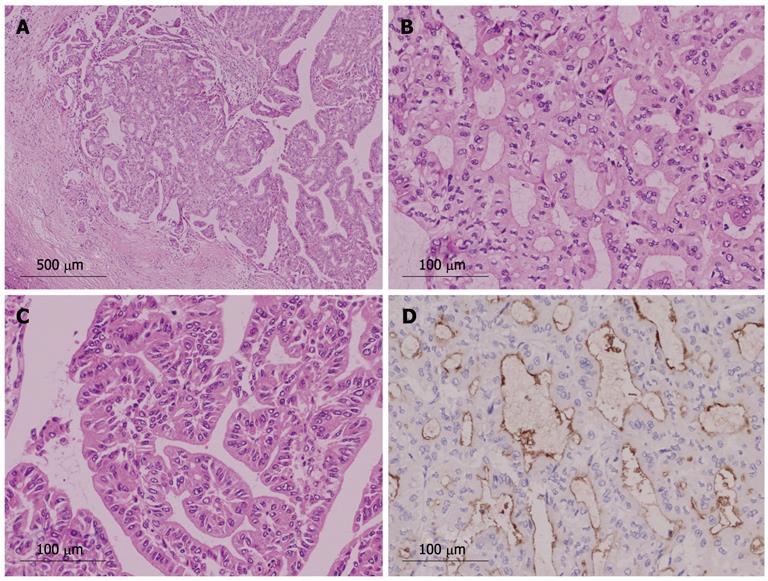
Figure 5 Histology of intraductal neoplasm of the intrahepatic bile duct with papillary and tubular structure (case 1).
A: Histological structure was mainly tubular, but papillary structure was also present [hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain, × 40]; B: Tubular structure (HE stain, × 200); C: Papillary structure (HE stain, × 200); D: Tumor cells were positive for mucin (MUC)1 immunohistochemistry (MUC1 stain, × 200).
- Citation: Naito Y, Kusano H, Nakashima O, Sadashima E, Hattori S, Taira T, Kawahara A, Okabe Y, Shimamatsu K, Taguchi J, Momosaki S, Irie K, Yamaguchi R, Yokomizo H, Nagamine M, Fukuda S, Sugiyama S, Nishida N, Higaki K, Yoshitomi M, Yasunaga M, Okuda K, Kinoshita H, Nakayama M, Yasumoto M, Akiba J, Kage M, Yano H. Intraductal neoplasm of the intrahepatic bile duct: Clinicopathological study of 24 cases. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(28): 3673-3680
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i28/3673.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i28.3673