Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2012; 18(27): 3527-3536
Published online Jul 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i27.3527
Published online Jul 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i27.3527
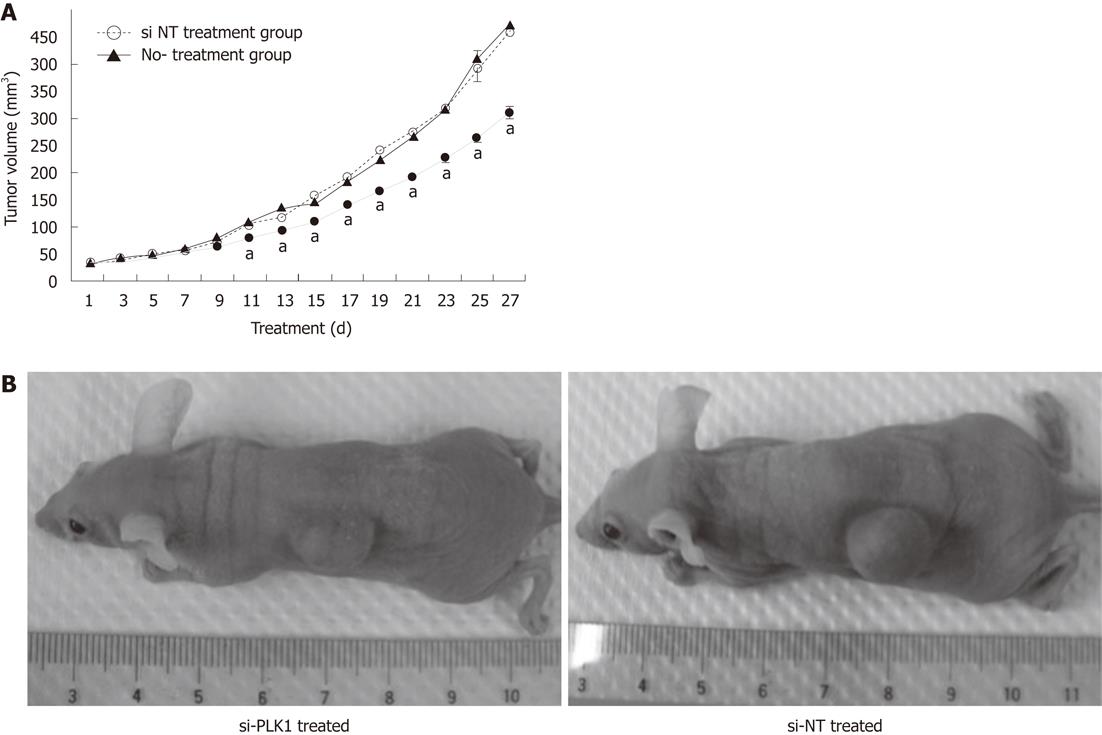
Figure 5 Reduction in hepatocellular carcinoma tumor size with knockdown of polo-like kinase 1.
A: Treatment of short-interfering RNA (siRNA) against polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) (si-PLK1, n = 6) in nude mice impeded the tumor growth compared with short interfering non-targeting (si-NT) (n = 6) or the non-treatment group (n = 6). Huh-7 tumor-bearing nude mice were treated with 1 nmol/L si-PLK1 intratumoral injections every alternate day for 27 d. Data are shown as mean ± SE, using the Student t-test (aP < 0.05); B: Images of nude mice with their tumors at day 27. The left panel shows a reduction in tumor size of subcutaneous tumors in nude mice treated with si-PLK1, while the right panel shows similar mice treated with si-NT.
- Citation: Mok WC, Wasser S, Tan T, Lim SG. Polo-like kinase 1, a new therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(27): 3527-3536
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i27/3527.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i27.3527