Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2012; 18(25): 3254-3259
Published online Jul 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i25.3254
Published online Jul 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i25.3254
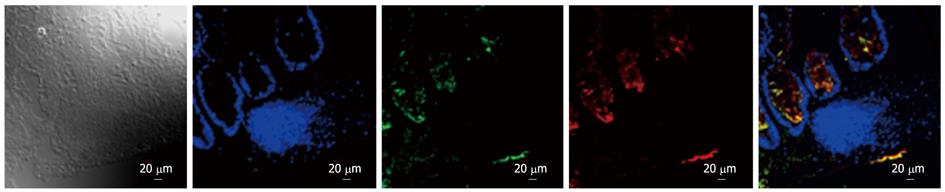
Figure 3 Localization of intestinal alkaline phosphatase and Toll-like receptor-4 in colon of Crohn’s disease.
Immunofluorescent staining for intestinal alkaline phosphatase (iAP) (red) and Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) (green) staining was performed in inflamed colon of patient with Crohn’s disease. Yellow color (merge) indicates co-localization of iAP and TLR4. For the observation of non-labeled tissues, differential interference contrast was used. Nuclei are stained with blue.
- Citation: Molnár K, Vannay &, Szebeni B, Bánki NF, Sziksz E, Cseh &, Győrffy H, Lakatos PL, Papp M, Arató A, Veres G. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase in the colonic mucosa of children with inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(25): 3254-3259
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i25/3254.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i25.3254