Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2012; 18(23): 2995-3003
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2995
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2995
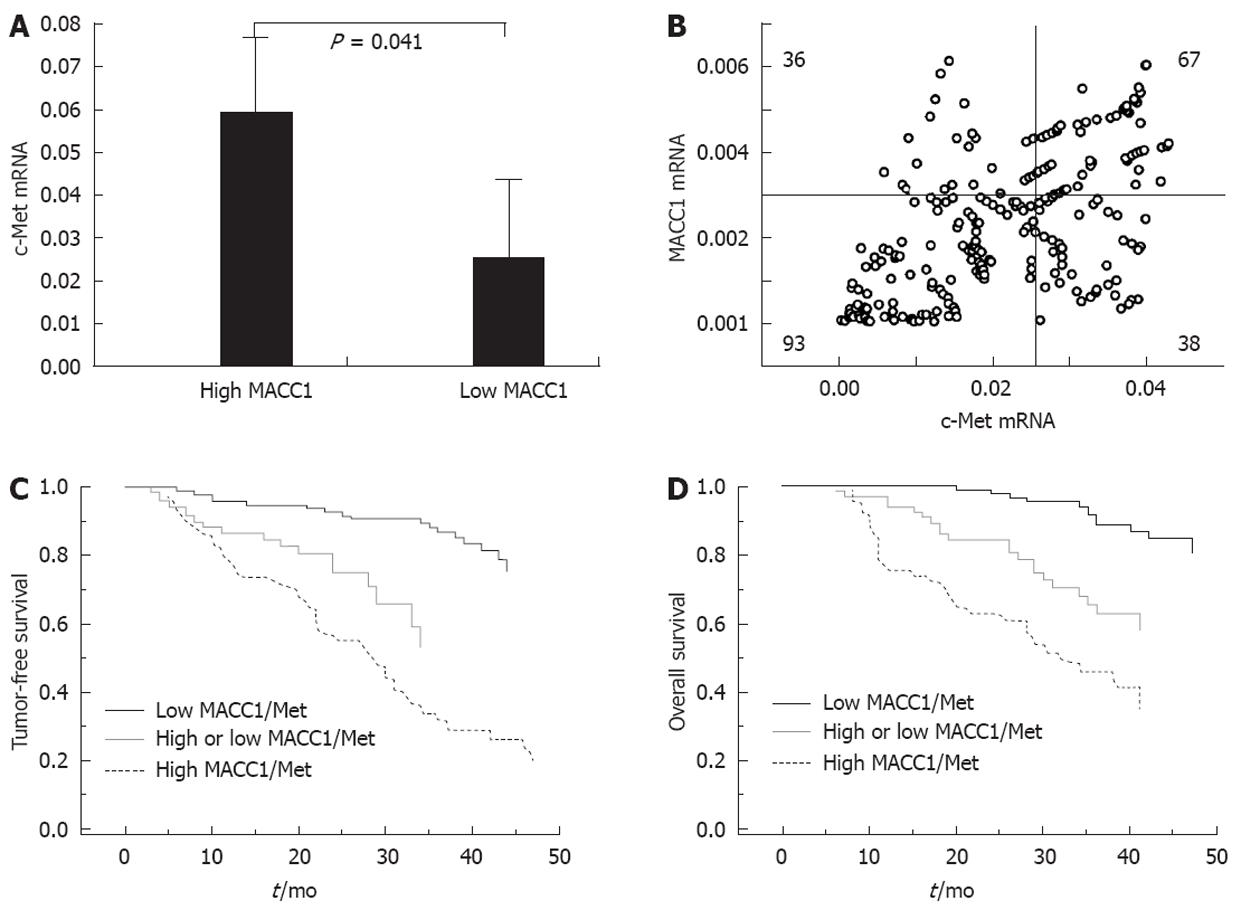
Figure 2 c-Met expression and correlation with metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 in 234 hepatocellular carcinoma patients received resection.
A: Comparison of c-Met expression level in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with high or low intratumoral metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 (MACC1) mRNA expression; B: c-Met level from 234 HCC patients receiving resection specimens were plottered against MACC1 levels from the same patients. Linear regression analysis showed a significant positive correlation between c-Met and MACC1 (r = 0.360, P < 0.001); C: Kaplan-Meier analysis of MACC1 and c-Met co-expression effects on tumor-free survival; D: Kaplan-Meier analysis of MACC1 and c-Met co-expression effects on overall survival.
- Citation: Qu JH, Chang XJ, Lu YY, Bai WL, Chen Y, Zhou L, Zeng Z, Wang CP, An LJ, Hao LY, Xu GL, Gao XD, Lou M, Lv JY, Yang YP. Overexpression of metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 predicts a poor outcome of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(23): 2995-3003
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i23/2995.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2995