Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2012; 18(23): 2938-2947
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2938
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2938
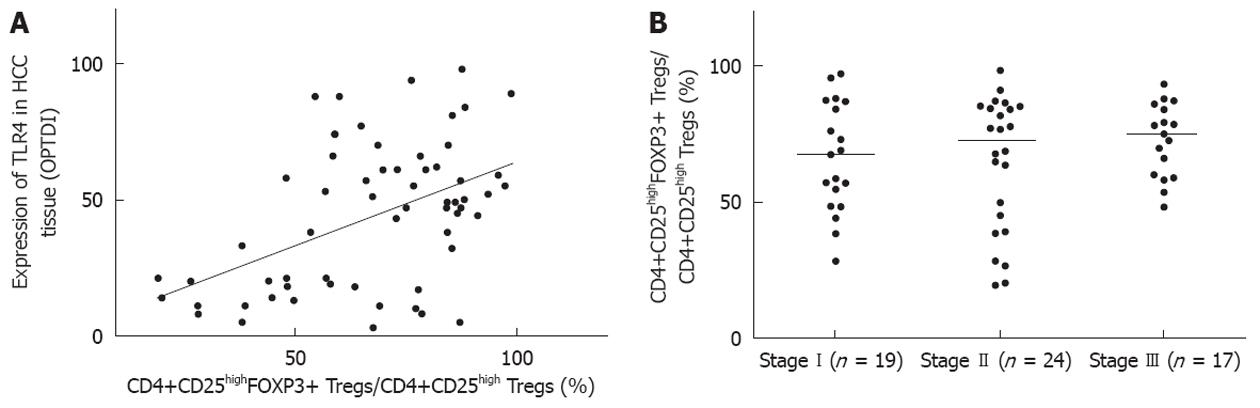
Figure 5 Correlation between the expression of toll-like receptor 4 in hepatocellular carcinoma specimens, tumor Union for International Cancer Control stage, and CD4+CD25high FOXP3+ regulatory T cell.
A: Toll-like receptor 4 expression was positively correlated with the number of CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) in peripheral blood. Analysis of data was performed using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients (n = 60, r = 0.411, P < 0.001); B: According to Union for International Cancer Control/tumor-node-metastasis classification, there were 19 cases, 24 cases, and 17 cases at stage I, II and III hepatocellular carcinoma, respectively. Statistically negative correlations were found in all comparisons between the 3 groups (χ2 = 0.921, P = 0.631) using the Kruskal-Wallis test.
-
Citation: Yang J, Zhang JX, Wang H, Wang GL, Hu QG, Zheng QC. Hepatocellular carcinoma and macrophage interaction induced tumor immunosuppression
via Treg requires TLR4 signaling. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(23): 2938-2947 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i23/2938.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2938