Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2012; 18(23): 2938-2947
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2938
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2938
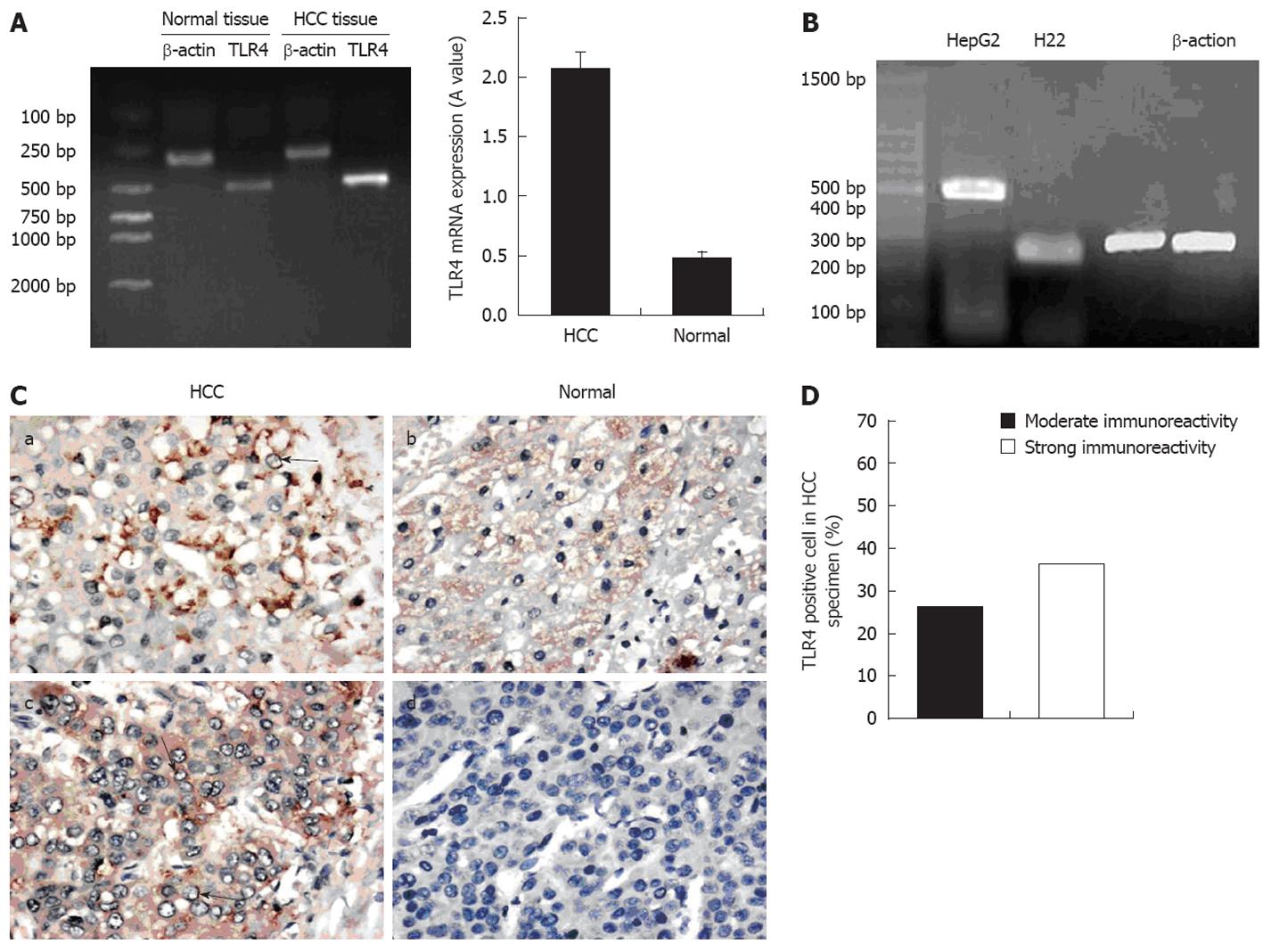
Figure 3 Expression of toll-like receptor 4 mRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma patients and hepatoma cell lines.
A: Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analysis of total RNA from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and normal tissues. The toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) mRNA expression in HCC tissues was stronger (2.08 ± 0.14) compared to normal tissues (0.48 ± 0.05) (P = 0.01); B: TLR4 mRNA expressed in human HepG2 and murine H22 hepatoma cell lines; C: Expression of TLR4 protein in HCC and normal tissues by immunohistochemistry. a, c: Paraffin-embedded sections of HCC exhibiting positive expression on the membrane and in the cytoplasm in several positive hepatocytes (arrows) [diaminobenzidine (DAB) ×400]; b, d: Paraffin-embedded sections of normal tissues showing weaker expression (DAB ×400); D: TLR4 was detected by immunohistochemistry in tissue sections of patients with HCC (frequency of positive hepatocytes for TLR4 in paraffin-embedded sections).
-
Citation: Yang J, Zhang JX, Wang H, Wang GL, Hu QG, Zheng QC. Hepatocellular carcinoma and macrophage interaction induced tumor immunosuppression
via Treg requires TLR4 signaling. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(23): 2938-2947 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i23/2938.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2938