Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2012; 18(23): 2914-2928
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2914
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2914
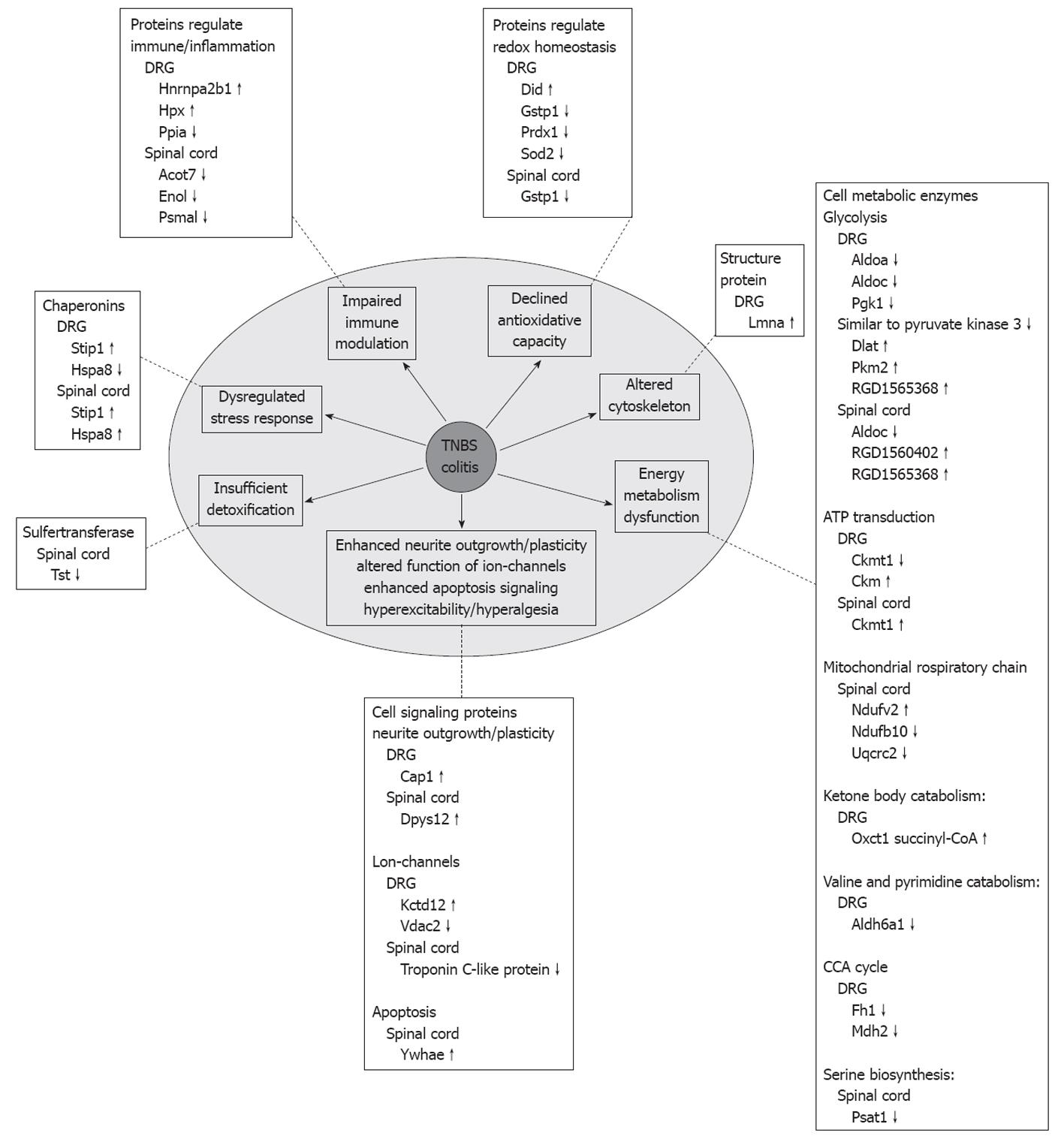
Figure 4 Schematic drawing summarizes the major findings that might associate with pathophysiological changes in rat nervous system caused by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis.
TNBS: Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid; DRG: Dorsal root ganglia; Hnrnpa2b1: Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A2/B1; Gstp1: Glutathione S-transferase P; Prdx1: Peroxiredoxin-1; Sod2: Superoxide dismutase; Lmna: Lamin C2; Aldoa: Aldolase A; Aldoc: Aldolase C; Ckmt1: Creatine kinase, mitochondrial 1, ubiquitous; Ckm: Creatine kinase M-type; Ndufv2: NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) flavoprotein 2; Ndufb10: NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 β subcomplex 10; Oxct1 succinyl-CoA: 3-ketoacid-coenzyme A transferase 1; Fh1: Fumarate hydratase; Mdh2: Malate dehydrogenase; Psat1: Phosphoserine aminotransferase; Cap1: Cyclase-associated protein 1; Kctd12: Potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing protein 12; Vdac2: Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2; Ywhae: The 14-3-3 protein epsilon; Tst: Thiosulfate sulfurtransferase; Stip1: Stress-induced phosphoprotein 1; Hspa8: heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein.
- Citation: Zhang XJ, Leung FP, Hsiao WW, Tan S, Li S, Xu HX, Sung JJ, Bian ZX. Proteome profiling of spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia in rats with trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(23): 2914-2928
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i23/2914.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2914