Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2012; 18(22): 2850-2858
Published online Jun 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2850
Published online Jun 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2850
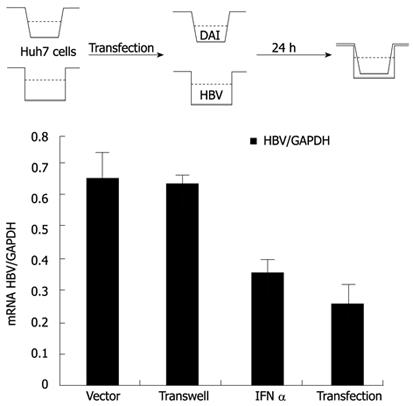
Figure 4 Inhibiting hepatitis B virus replication by DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors is an intracellular event.
Transwell co-culture experiment was performed: Huh7 cells were seeded in both 6-well plates (below) and transwells (top). In transwell co-culture group, pHBV1.3 was transfected into the cells in 6-well plates while hemagglutinin (HA)-DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors (DAI) was transfected into the cells in transwells. Twenty-four hours after the transfection, the cells in 6-well plates and transwells were co-cultured; in the direct cotransfection groups, pHBV1.3 and control DNA or HA-DAI were cotransfected into cells in 6-well plates; in interferon (IFN)-α treatment group, pHBV1.3 was transfected into the cells in 6-well plates, 1000 IU/mL IFN-α was added 12 h later. Seventy-two hours after transfection, all the cells were harvested and hepatitis B virus (HBV) RNA was determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Chen QY, Liu YH, Li JH, Wang ZK, Liu JX, Yuan ZH. DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors inhibits hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(22): 2850-2858
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i22/2850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2850