Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2012; 18(22): 2844-2849
Published online Jun 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2844
Published online Jun 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2844
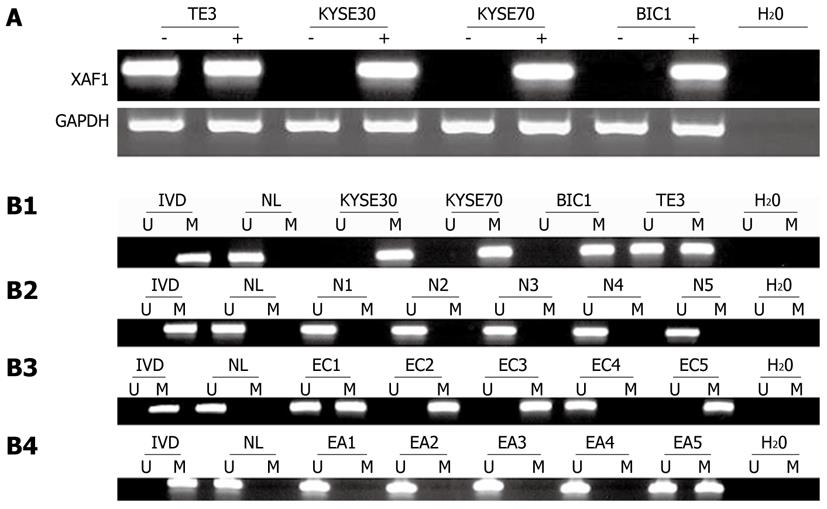
Figure 1 X chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor 1 expression was silenced by DNA methylation.
A: X chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor 1 (XAF1) expression was analyzed by semi-quantitative reverse transcriptional polymerase chain reaction before and after 5-aza-dc treatment (2 mol/L, 96 h) of the esophageal cancer cell lines (KYSE30, KYSE70, BIC1 and TE3). Methylation status of XAF1 CpG islands in esophageal cancer cell lines, esophageal normal mucosa, esophageal cancer tissue, and matched adjacent normal tissue. Primer efficiency was verified with a positive control (in vitro methylated DNA, IVD) and a negative control (normal blood lymphocyte DNA, NL). “U” indicates the presence of unmethylated alleles; “M” indicates the presence of methylated alleles; B1: Methylation of XAF1 in esophageal cancer cell lines (KYSE30, KYSE70, BIC1 and TE3); B2: Methylation of XAF1 in normal esophageal mucosa (NE1, NE2, NE3, NE4 and NE5); B3: Representative methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (MSP) results for XAF1 in esophageal primary cancer tissue samples (EC); B4: Representative MSP results for XAF1 in esophageal matched adjacent normal tissue (EA). GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Chen XY, He QY, Guo MZ. XAF1 is frequently methylated in human esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(22): 2844-2849
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i22/2844.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2844