Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2012; 18(20): 2502-2510
Published online May 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i20.2502
Published online May 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i20.2502
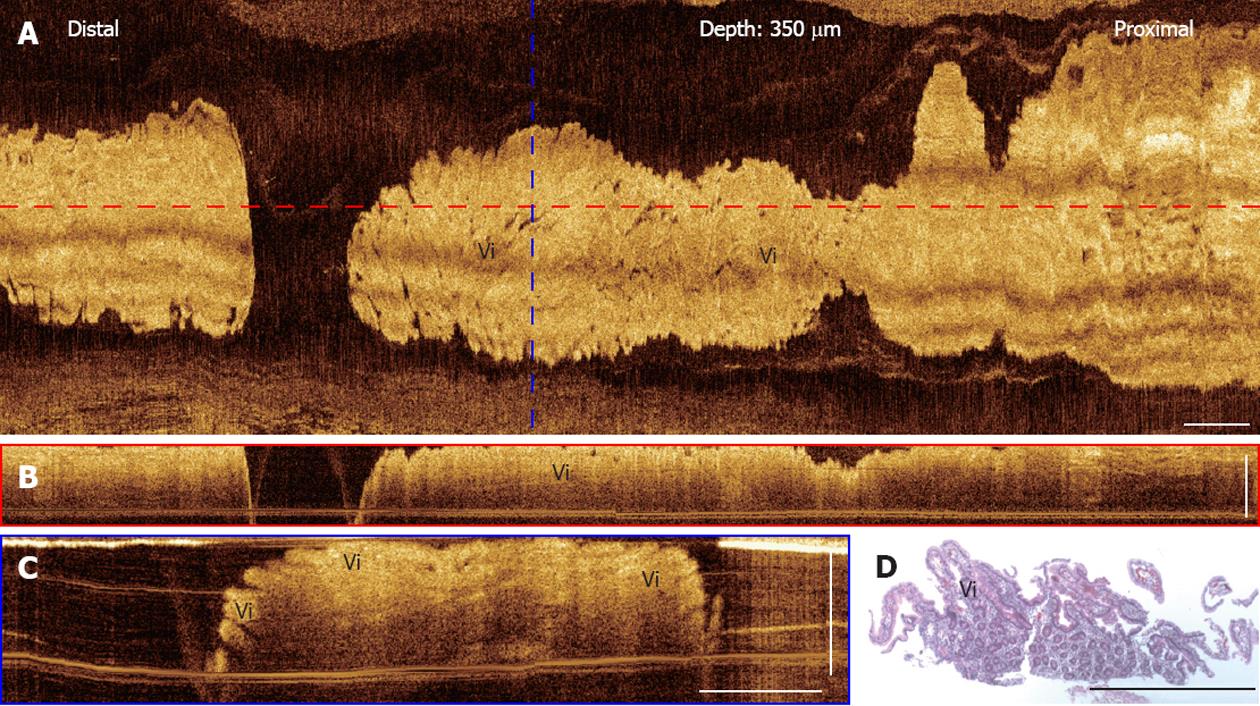
Figure 6 Three-dimensional-optical coherence tomography images of a normal duodenum.
A: En face projection optical coherence tomography (OCT) image at a depth of 350 μm; B: Cross-sectional OCT images of the duodenum along the probe pullback direction; C: Cross-sectional OCT image, corresponding to the blue dashed line marked in (A); Mucosal villous structures (Vi) in the duodenum are clearly seen; D: Corresponding histology of the duodenum showing the villi. Scale bars: 1 mm.
- Citation: Zhou C, Kirtane T, Tsai TH, Lee HC, Adler DC, Schmitt JM, Huang Q, Fujimoto JG, Mashimo H. Cervical inlet patch-optical coherence tomography imaging and clinical significance. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(20): 2502-2510
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i20/2502.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i20.2502