Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2012; 18(19): 2383-2389
Published online May 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2383
Published online May 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2383
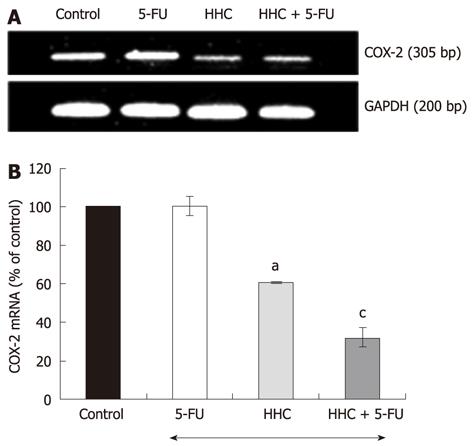
Figure 4 Combination effects of hexahydrocurcumin and 5-fluorouracil on cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA expression in HT-29 colon cancer cells.
The HT-29 cells were exposed to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) (5 μmol/L), hexahydrocurcumin (HHC) (25 μmol/L) and their combination for 24 h. Cells from different experimental groups were subjected to semi-quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). A: RT-PCR showed that the expression of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 (305 bp) was significantly decreased in HHC or combination of HHC and 5-FU-treated group; B: The expression of COX-2 was determined by normalizing the band intensity of COX-2 with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Values are expressed as percentage of control (mean ± SE), aP < 0.05 vs control; cP < 0.05 vs 5-FU or HHC monotherapy (n = 3).
- Citation: Srimuangwong K, Tocharus C, Yoysungnoen Chintana P, Suksamrarn A, Tocharus J. Hexahydrocurcumin enhances inhibitory effect of 5-fluorouracil on HT-29 human colon cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(19): 2383-2389
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i19/2383.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2383