Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2012; 18(19): 2344-2356
Published online May 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2344
Published online May 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2344
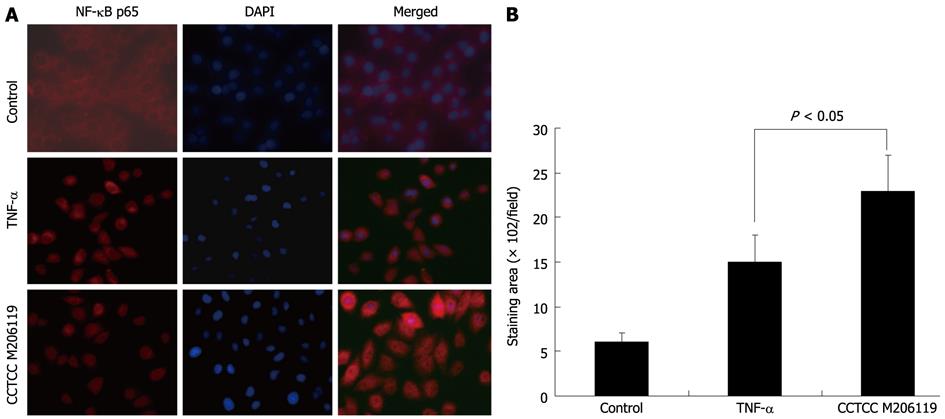
Figure 3 Effects of China Center for Type Culture Collection M206119 strain on epithelial injury and translocation of nuclear factor-κB in vitro.
Immunofluorescence staining for nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65 (red) and 4',6'-diamidino-2-phenylindole hydrochloride (DAPI) (blue) in HT-29 cells treated either by tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α or China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) M206119 (scale bars, 10 mm). A: Increased positive NF-κB p65 staining after CCTCC M206119 treatment; B: Positive staining areas were quantified as pixels per high-power microscopic field (400 ×) using Photoshop. Error bars indicate mean ± SD (n = 3).
-
Citation: Zhou FX, Chen L, Liu XW, Ouyang CH, Wu XP, Wang XH, Wang CL, Lu FG.
Lactobacillus crispatus M206119 exacerbates murine DSS-colitis by interfering with inflammatory responses. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(19): 2344-2356 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i19/2344.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2344