Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2012; 18(19): 2344-2356
Published online May 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2344
Published online May 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2344
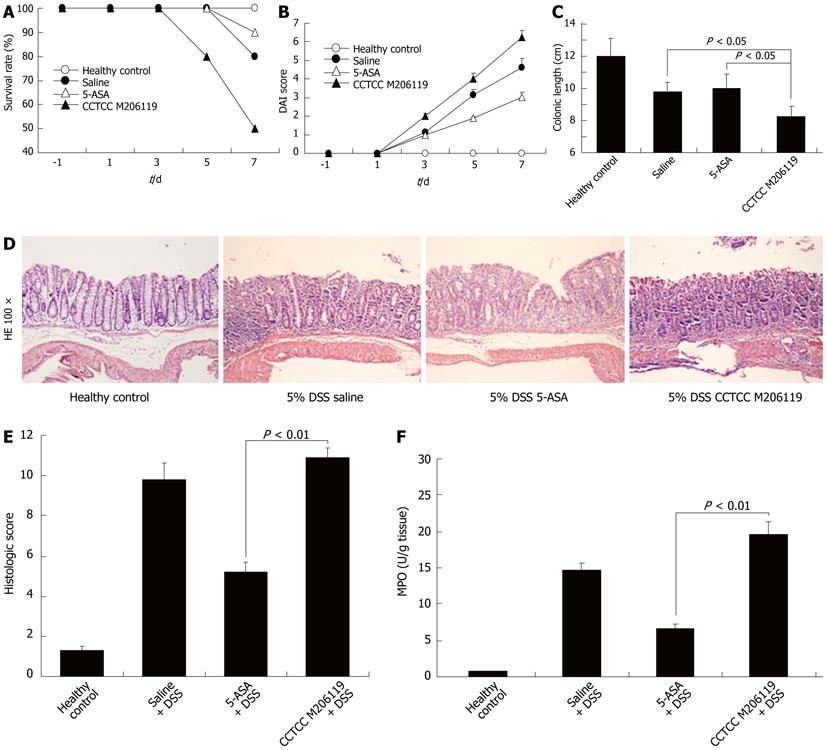
Figure 1 Colonic inflammation was aggravated in dextran sulfate sodium-colitis mice after China Center for Type Culture Collection M206119 treatment.
A: Survival rate changes of four age- and sex-matched BALB/c mouse groups (n = 10) [〇: Healthy controls; ●: 5% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) plus saline treatment; △: 5% DSS plus 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) treatment; ▲: 5% DSS plus China Center for Type Culture Collection M206119] at the indicated time points; B: Disease activity index (DAI) changes among groups in (A) after 7 d 5% DSS treatment at the indicated time points. Each point represents the mean ± SE (n = 10); C: Mean colon length (cm) for the mice in (A); D: Histological analysis of representative colons from the mice in (A) (original magnification, hematoxylin and eosin staining, 100 ×); E: Summarized histological scores from colons of (D); F: Summarized myeloperoxidase (MPO) activities of colons from mice in (D).
-
Citation: Zhou FX, Chen L, Liu XW, Ouyang CH, Wu XP, Wang XH, Wang CL, Lu FG.
Lactobacillus crispatus M206119 exacerbates murine DSS-colitis by interfering with inflammatory responses. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(19): 2344-2356 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i19/2344.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2344