Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2012; 18(18): 2245-2252
Published online May 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2245
Published online May 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2245
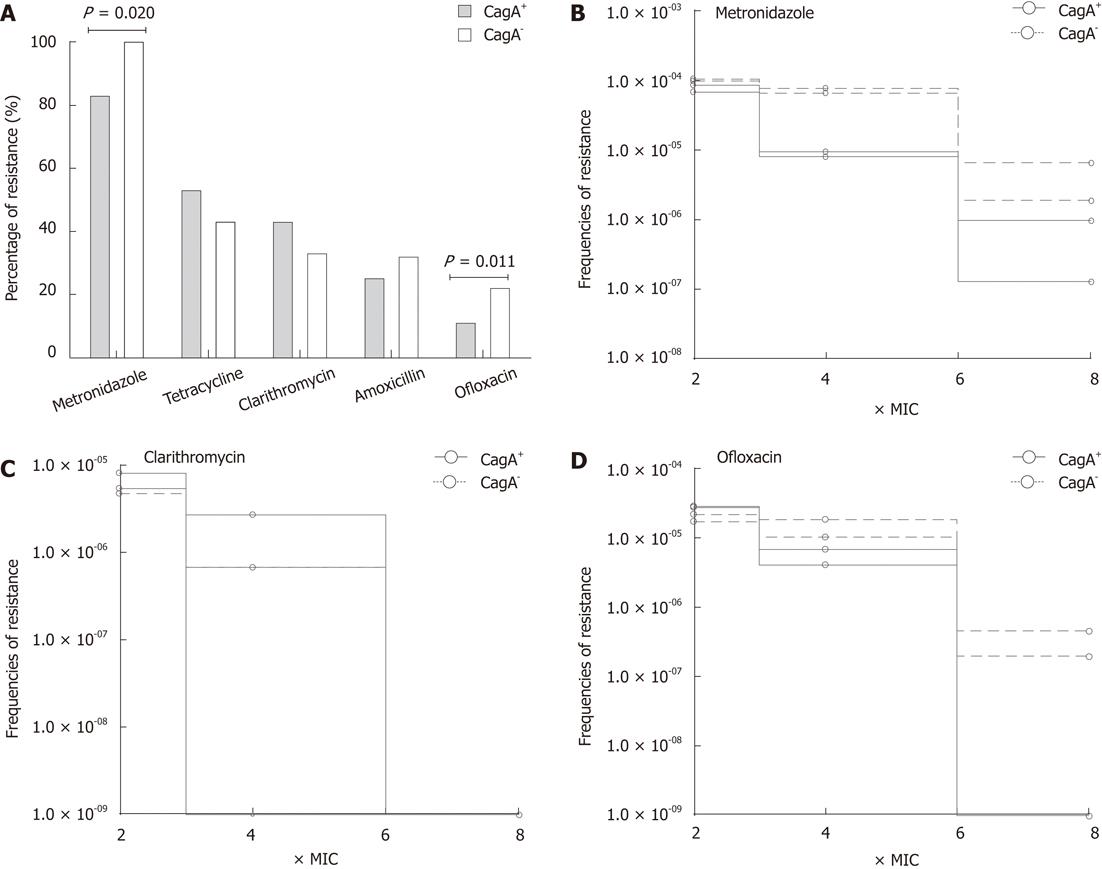
Figure 4 The correlation of antimicrobial drug resistance with cagA gene.
A: Rate of drug resistance in Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) strains carrying (n = 81) and devoid of (n = 72) of cagA gene. Statistical differences were observed by Pearson’s χ2 test. To determine the effect of cagA carriage on the development of resistance, cagA+ (n = 2) and cagA- (n = 2) H. pylori strains were exposed to the increasing concentrations of metronidazole (B) clarithromycin (C) and ofloxacin (D). Bacterial growth was monitored at different concentration of antibiotic and frequencies of resistant mutants were determined as the colony forming units of H. pylori strain divided by the starting inocula.
-
Citation: Khan A, Farooqui A, Manzoor H, Akhtar SS, Quraishy MS, Kazmi SU. Antibiotic resistance and
cagA gene correlation: A looming crisis ofHelicobacter pylori . World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(18): 2245-2252 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i18/2245.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2245