Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2012; 18(18): 2147-2160
Published online May 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147
Published online May 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147
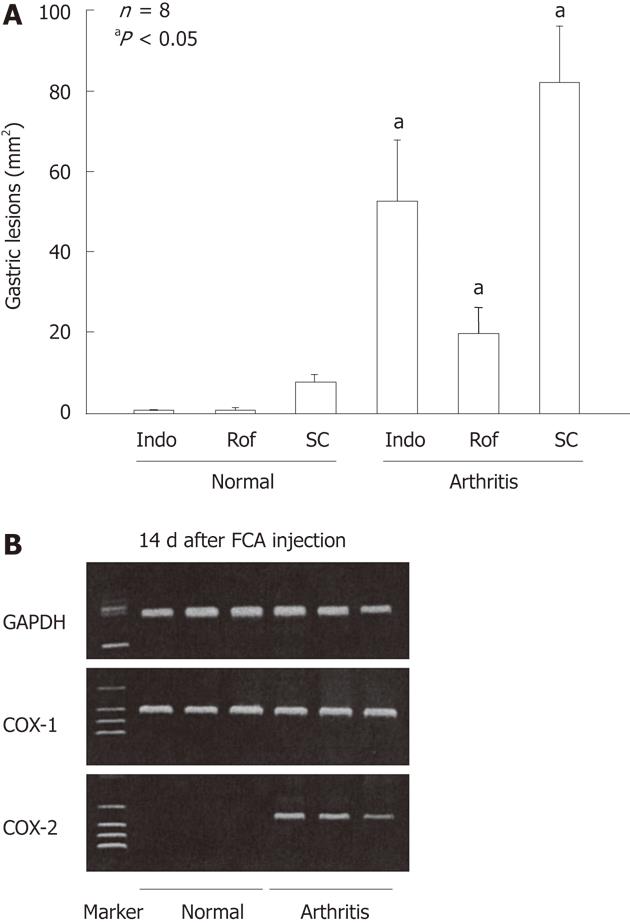
Figure 13 Gastric ulcerogenic effect of indomethacin, rofecoxib and SC-560 and the expression of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in the gastric mucosa of normal and arthritic rats.
A: Arthritis was induced by injecting Freund’s complete adjuvant (FCA) into the plantar region of the right hindfoot, and the experiments were performed 14 d after the injection. Indomethacin (Indo) (3 mg/kg), rofecoxib (Rof) (30 mg/kg), or SC-560 (SC) (30 mg/kg) were administered p.o., and the animals were killed 4 h later. Data are presented as the mean ± SE in 4-8 animals, aP < 0.05 vs the corresponding group in normal rats; B: COX-2 mRNA was not detected in the normal rats, but clearly observed in the arthritic rats on day 14 after the FCA injection, whereas COX-1 mRNA was observed in the stomach of both normal and arthritic rats. Lane 1, marker; lanes 2-4, normal rats; lanes 5-7, arthritic rats (data from ref. 23 after modification). GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Takeuchi K. Pathogenesis of NSAID-induced gastric damage: Importance of cyclooxygenase inhibition and gastric hypermotility. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(18): 2147-2160
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i18/2147.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147