Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2012; 18(18): 2147-2160
Published online May 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147
Published online May 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147
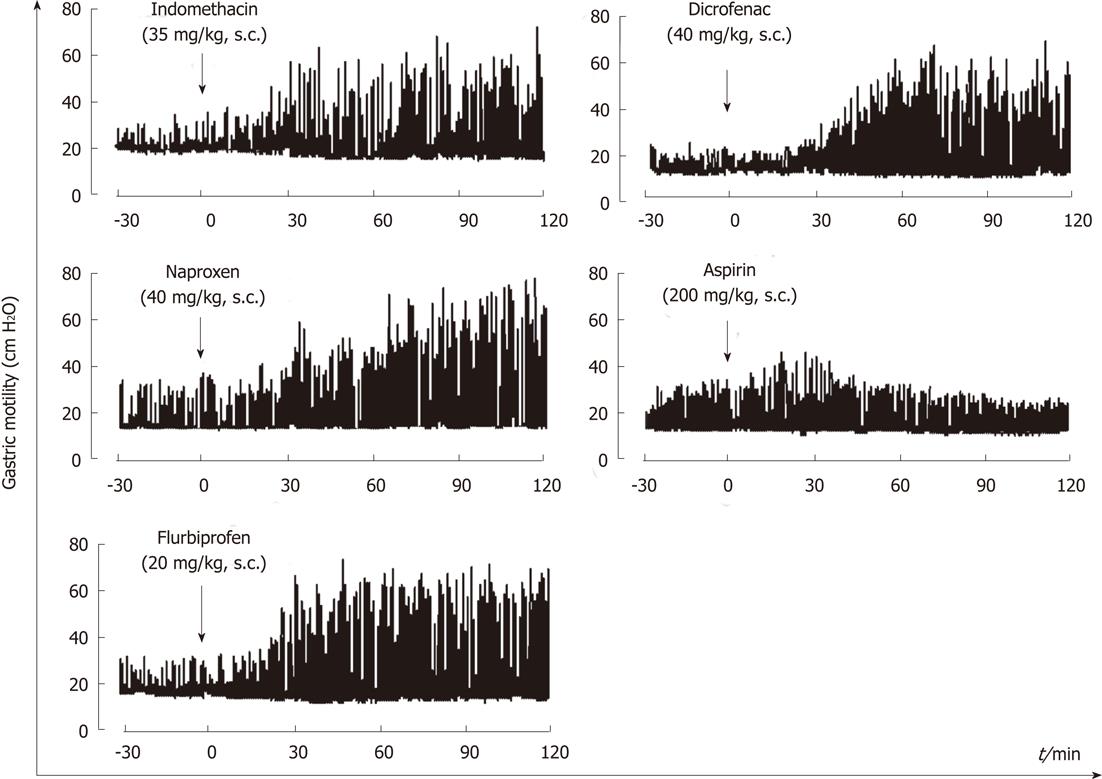
Figure 3 Representative recordings showing the effects of various non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug on gastric motility in rats.
Indomethacin (35 g/kg), aspirin (200 mg/kg), naproxen (40 mg/kg), flurbiprofen (20 mg/kg) or diclofenac (40 mg/kg) was given s.c. after basal motility had stabilized (data from ref.18 after modification).
- Citation: Takeuchi K. Pathogenesis of NSAID-induced gastric damage: Importance of cyclooxygenase inhibition and gastric hypermotility. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(18): 2147-2160
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i18/2147.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147