Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2012; 18(17): 2084-2091
Published online May 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i17.2084
Published online May 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i17.2084
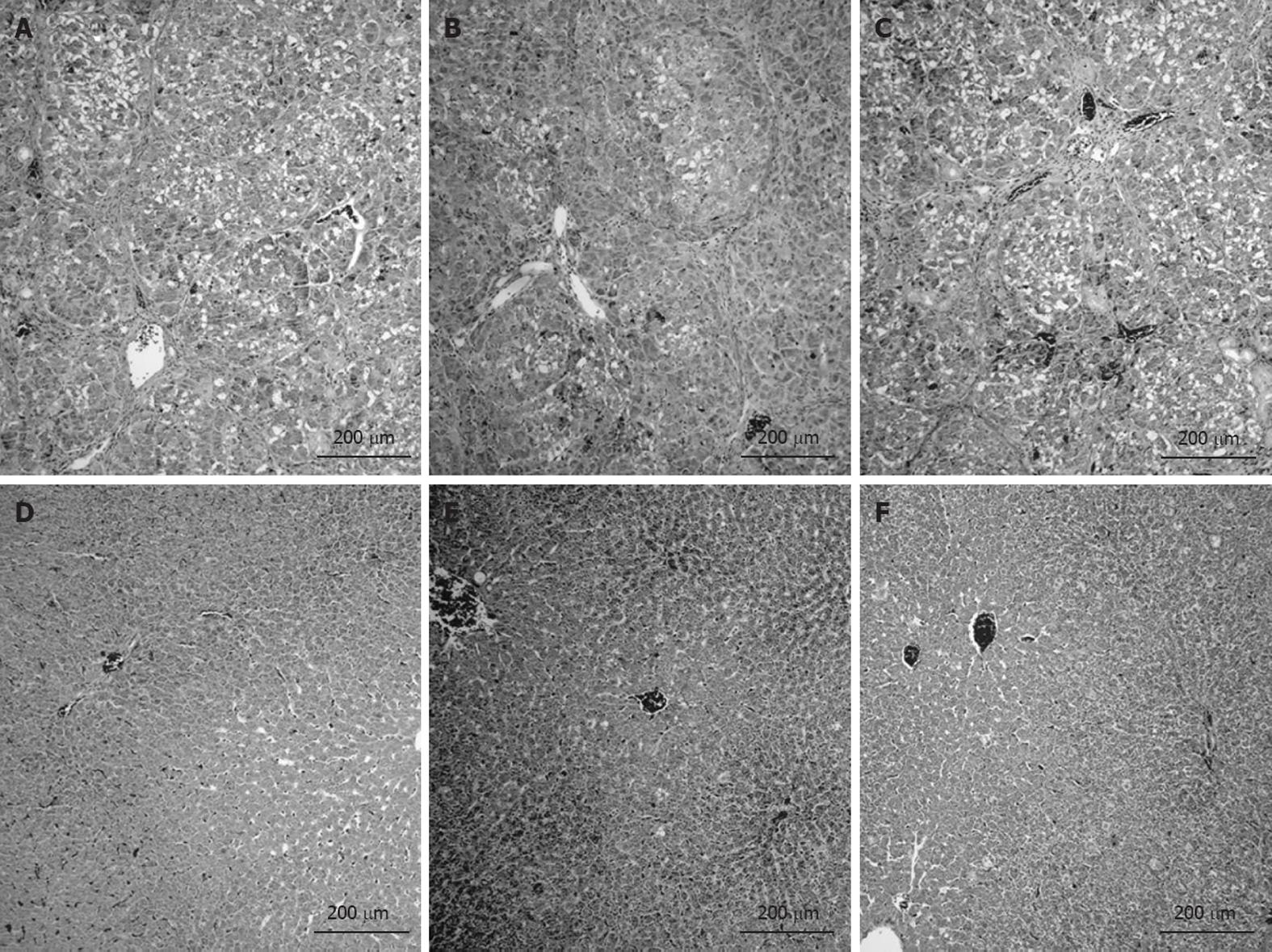
Figure 6 Photomicrographs of liver sections.
All cirrhotic rats developed micronodular cirrhosis with regeneration nodules, necrosis and steatosis regardless of treatment (A: Cirrhosis; B: Cirrhosis + IGF-1; C: Cirrhosis + rifaximin). All control rats showed normal cellular architecture (D: Control; E: Control + IGF-1; F: Control + rifaximin).
- Citation: Òdena G, Miquel M, Serafín A, Galan A, Morillas R, Planas R, Bartolí R. Rifaximin, but not growth factor 1, reduces brain edema in cirrhotic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(17): 2084-2091
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i17/2084.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i17.2084