Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2012; 18(17): 2035-2042
Published online May 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i17.2035
Published online May 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i17.2035
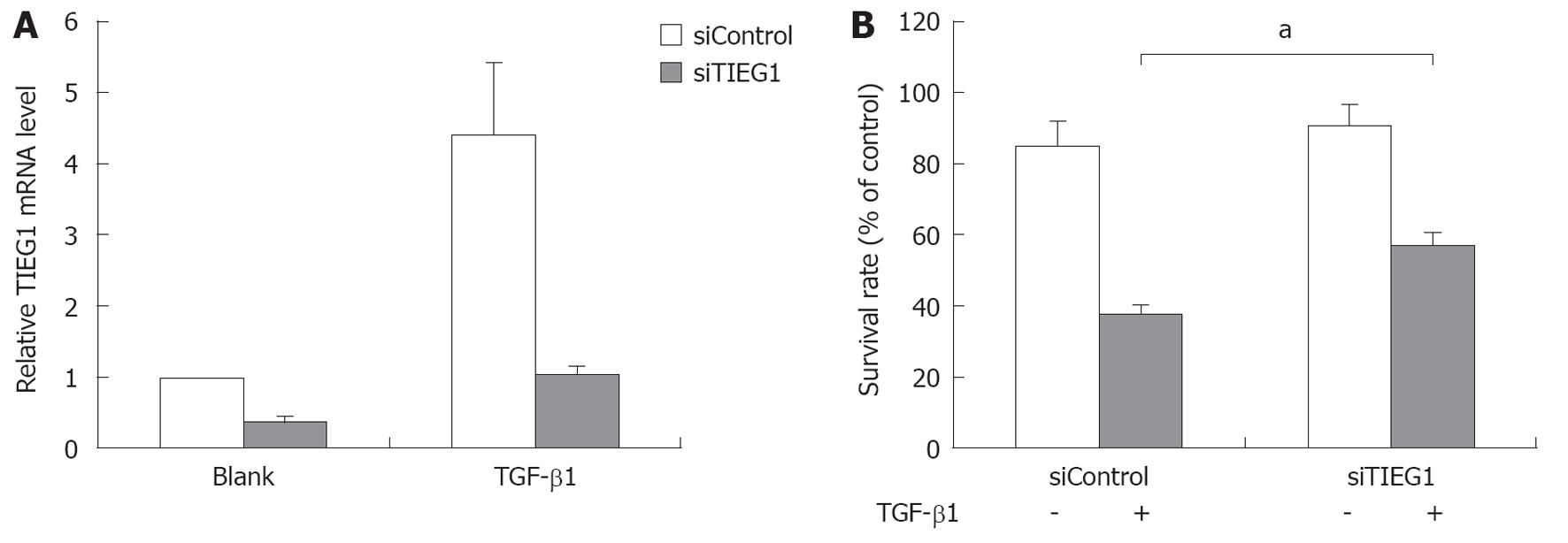
Figure 3 Downregulation of transforming growth factor-β-inducible early gene 1 by RNA interference (siRNA) decreased the transforming growth factor-β1 susceptibility of Hep3B cells.
A: Decreases in the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β-inducible early gene 1 (TIEG1) mRNA level in siRNAs targeting TIEG1 (siTIEG1)-transfected Hep3B cells with or without TGF-β1 treatment. Cells were transfected with siTIEG1 prior to the TGF-β1 treatments described above. After 4 h of treatment, mRNA levels of TIEG1 were determined by quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction; B: Increases in the survivability of the siTIEG1-transfected and the TGF-β1-treated Hep3B cells. The decreased growth inhibitory response of Hep3B cells to TGF-β1 treatment was determined by methylthiazoletetrazolium assays after 72 h of TGF-β1 treatment. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Jiang L, Lai YK, Zhang JF, Chan CY, Lu G, Lin MC, He ML, Li JC, Kung HF. Transactivation of the TIEG1 confers growth inhibition of transforming growth factor-β-susceptible hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(17): 2035-2042
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i17/2035.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i17.2035