Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2012; 18(16): 1892-1902
Published online Apr 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i16.1892
Published online Apr 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i16.1892
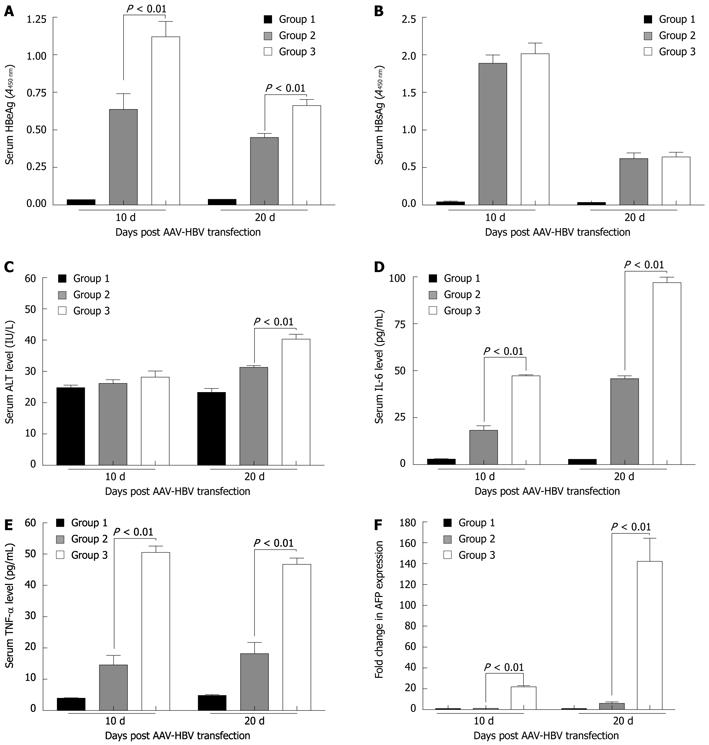
Figure 6 Comparison of the serum hepatitis B e antigen, hepatitis B surface antigen, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, alanine aminotransferase levels and hepatic α-fetoprotein mRNA levels between mice from different groups.
Group 1: Adeno-associated virus (AAV)-internal ribosome entry site transfected doxycycline (Dox)-induced in-alb-urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) mice (n = 6); Group 2: AAV-hepatitis B virus (HBV) transfected non-induced in-alb-uPA mice (n = 6); Group 3: AAV-HBV transfected Dox-induced in-alb-uPA mice (n = 6). HBeAg: Hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; AFP: α-fetoprotein.
- Citation: Zhou XJ, Sun SH, Wang P, Yu H, Hu JY, Shang SC, Zhou YS. Over-expression of uPA increases risk of liver injury in pAAV-HBV transfected mice. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(16): 1892-1902
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i16/1892.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i16.1892