Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2012; 18(16): 1892-1902
Published online Apr 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i16.1892
Published online Apr 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i16.1892
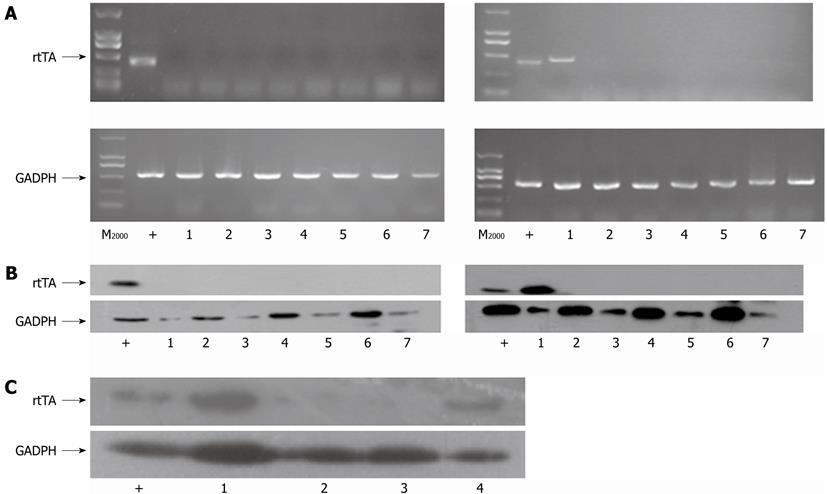
Figure 3 The specific expression of tetracycline reverse transcriptional activator in the livers of albumin-tetracycline reverse transcriptional activatortrangenic mice and in-alb-urokinase plasminogen activator transgenic mice.
A, B: Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (A) and Western blotting (B) analysis of tetracycline reverse transcriptional activator (rtTA) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) expression in different tissues of the 6-8 wk old F1 albumin-rtTA PCR-negative (left for A, B) or positive (right for A, B) transgenic mice. 1: Liver; 2: Brain; 3: Thymus; 4: Heart; 5: Lung; 6: Kidney; 7: Spleen; C: Western blotting analysis of rtTA and GADPH expression in the liver extracts of mice with different genotypes.1: In-alb-urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) mice group; 2: Liver extracts of wild type mice group; 3: tetO-uPA mice group; 4: Albumin-rtTA mice group. pTet-on transfected Huh7 cell extracts were used as positive control (+).
- Citation: Zhou XJ, Sun SH, Wang P, Yu H, Hu JY, Shang SC, Zhou YS. Over-expression of uPA increases risk of liver injury in pAAV-HBV transfected mice. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(16): 1892-1902
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i16/1892.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i16.1892