Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2012; 18(16): 1884-1891
Published online Apr 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i16.1884
Published online Apr 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i16.1884
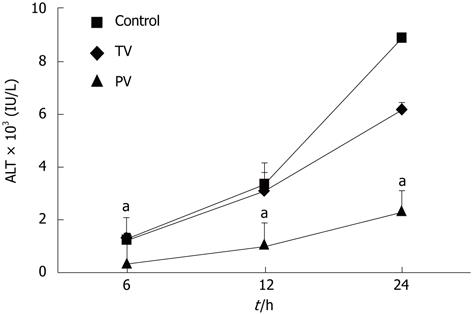
Figure 1 Effects of antithrombin III on serum alanine aminotransferase levels in rats with acute liver failure.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and D-galactosamine (GalN) were injected intraperitoneally into 8-wk-old Wistar rats. One hour after the challenge, antithrombin (AT) III (50 U/kg body weight) was injected into the portal or tail vein. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels were measured at 6 h, 12 h and 24 h after injection of LPS and GalN. Control: Untreated; TV: AT III injection via the tail vein; PV: AT III injection via the portal vein. Values are mean ± SD (n = 10 rats/group). aP < 0.01 vs the control group.
-
Citation: Miyazaki M, Kato M, Tanaka M, Tanaka K, Takao S, Kohjima M, Ito T, Enjoji M, Nakamuta M, Kotoh K, Takayanagi R. Antithrombin III injection
via the portal vein suppresses liver damage. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(16): 1884-1891 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i16/1884.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i16.1884