Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2012; 18(15): 1781-1788
Published online Apr 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i15.1781
Published online Apr 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i15.1781
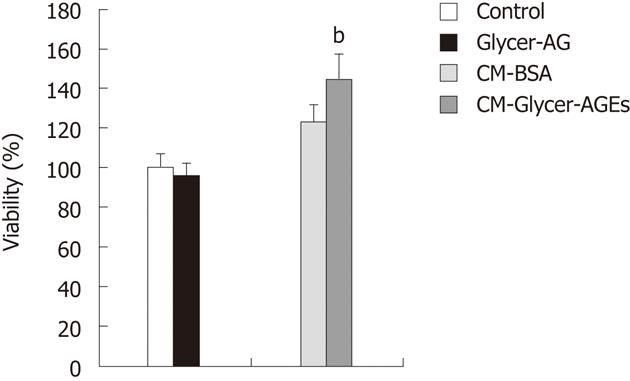
Figure 5 Effect of glyceraldehyde-derived advanced glycation end-products-treated CM on human umbilical vein endothelial cells proliferation.
Cell viability was determined with the WST-8 assay. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells were incubated with control unglycated bovine serum albumin (BSA), glyceraldehyde-derived advanced glycation end-products (Glycer-AGEs) (100 μg/mL), CM-BSA, or CM-Glycer-AGEs for 72 h. The open and filled bars represent results for cells treated with control unglycated BSA and Glycer-AGEs, respectively, and the light grey and the black grey bars represent results for cells treated with CM-BSA and CM-Glycer-AGEs, respectively. Data are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 6), bP < 0.01 vs CM-BSA.
- Citation: Takino J, Yamagishi S, Takeuchi M. Glycer-AGEs-RAGE signaling enhances the angiogenic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma by upregulating VEGF expression. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(15): 1781-1788
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i15/1781.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i15.1781