Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2012; 18(15): 1732-1744
Published online Apr 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i15.1732
Published online Apr 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i15.1732
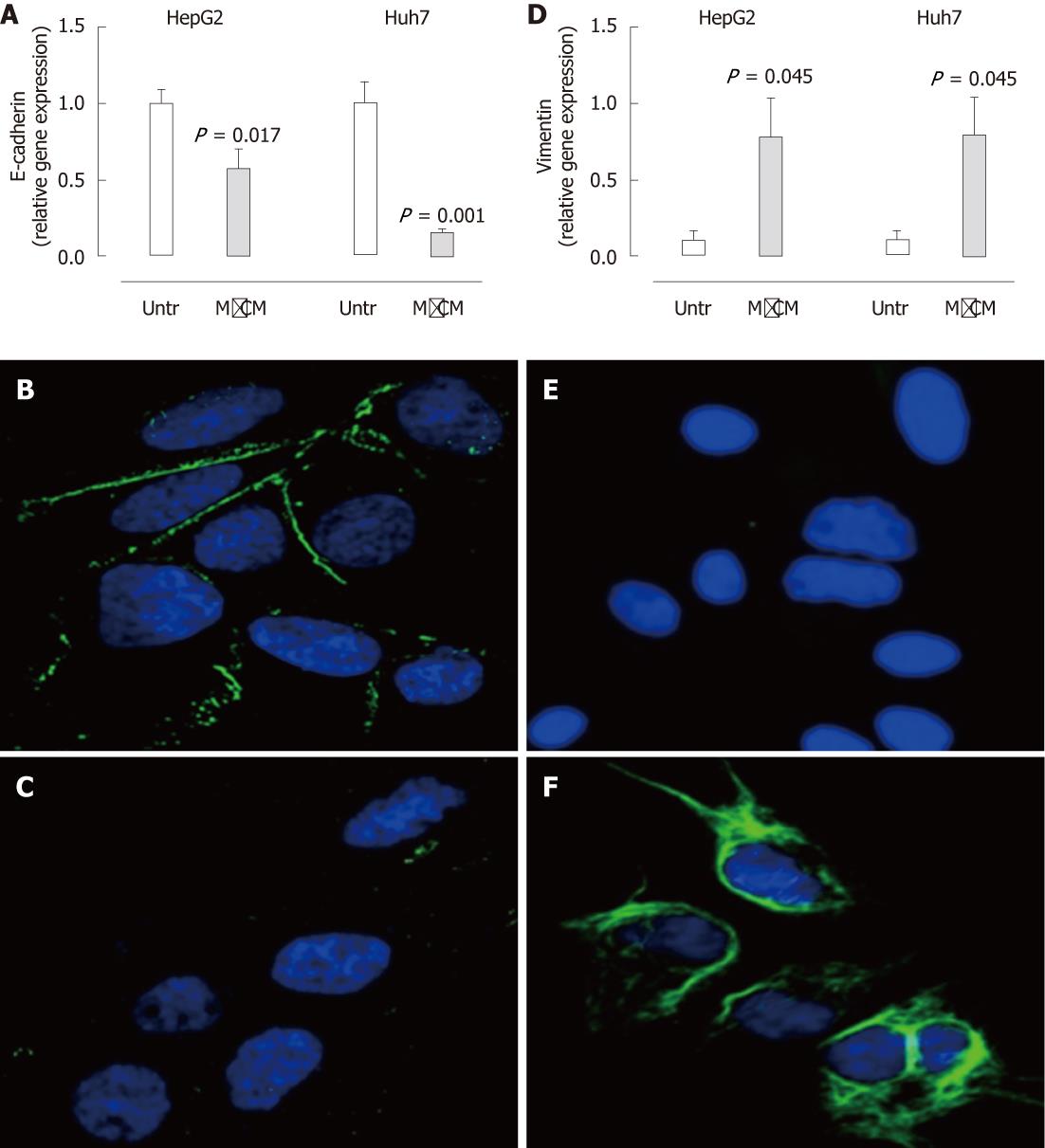
Figure 3 Expression of E-cadherin is reduced and vimentin is increased in hepatocytes treated with macrophage-conditioned media.
A, D: Following culture in complete media or 50% macrophage-conditioned media (MφCM) for 24 h, E-cadherin (A) and vimentin (D) mRNA levels in HepG2 and Huh7 cells were measured by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Results are expressed as fold of untreated cells (mean ± SEM, n = 8) (P < 0.05 vs untreated); B, C: Immunofluorescence staining for E-cadherin (green) in untreated (B) and MφCM-treated (C) Huh7 cells; E, F: Immunofluorescence staining for vimentin (green) in untreated (E) and MφCM-treated (F) Huh7 cells. 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole stained nuclei blue (63 × magnification). Untr: Untreated.
- Citation: Melino M, Gadd VL, Walker GV, Skoien R, Barrie HD, Jothimani D, Horsfall L, Jones A, Sweet MJ, Thomas GP, Clouston AD, Jonsson JR, Powell EE. Macrophage secretory products induce an inflammatory phenotype in hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(15): 1732-1744
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i15/1732.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i15.1732