Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2012; 18(13): 1508-1516
Published online Apr 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i13.1508
Published online Apr 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i13.1508
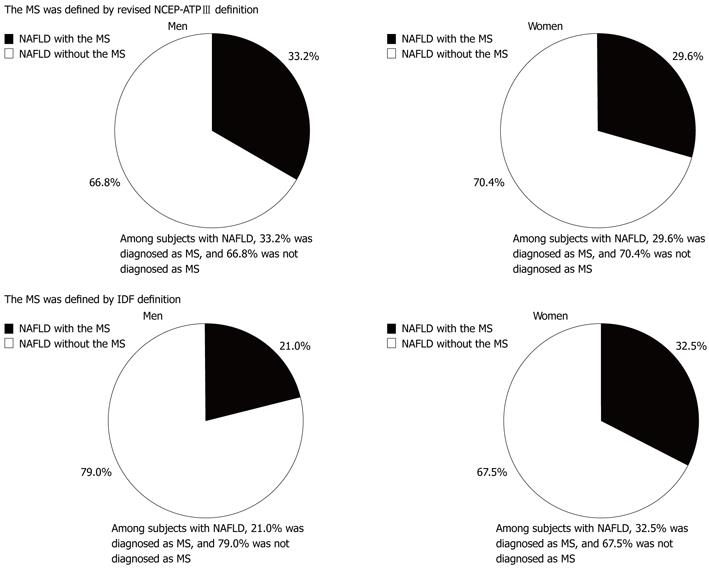
Figure 3 The prevalence of subjects with or without the metabolic syndrome among 1874 men and 514 women with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Data was expressed as prevalence (%). The metabolic syndrome (MS) was diagnosed using revised IDF. Among men with NAFLD, 66.8% and 79.0% were not diagnosed with the MS defined by revised NCEP-ATPIII definition and revised IDF definition, respectively. In women, 70.4% and 67.5%, respectively, were not diagnosed with the MS by revised NCEP-ATPIII definition and revised IDF definition. IDF: International Diabetes Federation; NCEP-ATPIII: National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Citation: Hamaguchi M, Takeda N, Kojima T, Ohbora A, Kato T, Sarui H, Fukui M, Nagata C, Takeda J. Identification of individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by the diagnostic criteria for the metabolic syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(13): 1508-1516
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i13/1508.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i13.1508