Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2012; 18(10): 1059-1066
Published online Mar 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1059
Published online Mar 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1059
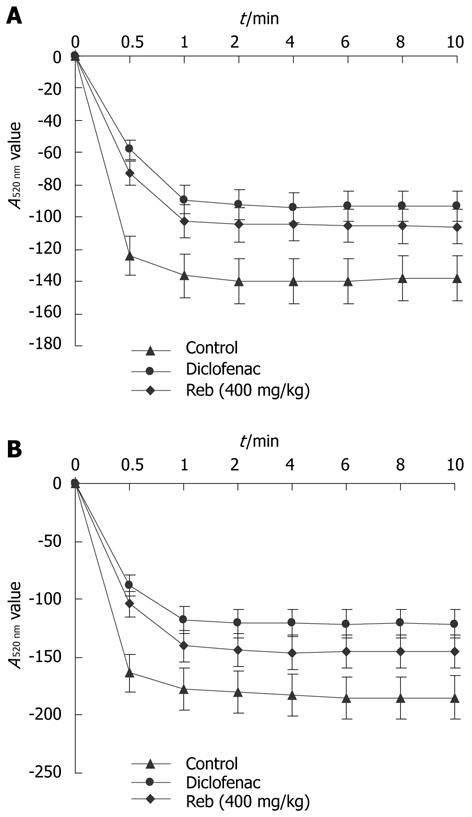
Figure 5 Effects of rebamipide on diclofenac-induced liver mitochondrial swelling in mice.
A: After adding the reaction buffer, the absorbance at 520 nm in the control mitochondria declined rapidly. The decrease was smaller in the presence of diclofenac compared with that in the control, demonstrating that liver mitochondrial dysfunction was induced by diclofenac administration. This reduction in absorbance was significantly increased in the presence of rebamipide, indicating that rebamipide improved impaired mitochondrial function; B: After adding 0.3 mmol/L CaC12 reaction buffer, the absorbance at 520 nm in the control mitochondria declined rapidly, suggesting significant swelling of mitochondria. The decrease was smaller in the presence of diclofenac compared with that in the control, demonstrating that liver mitochondrial dysfunction was induced by diclofenac administration. This reduction was significantly increased in the presence of rebamipide, indicating that rebamipide improved impaired mitochondrial function.
-
Citation: Diao L, Mei Q, Xu JM, Liu XC, Hu J, Jin J, Yao Q, Chen ML. Rebamipide suppresses diclofenac-induced intestinal permeability
via mitochondrial protection in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(10): 1059-1066 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i10/1059.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1059