Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2012; 18(10): 1059-1066
Published online Mar 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1059
Published online Mar 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1059
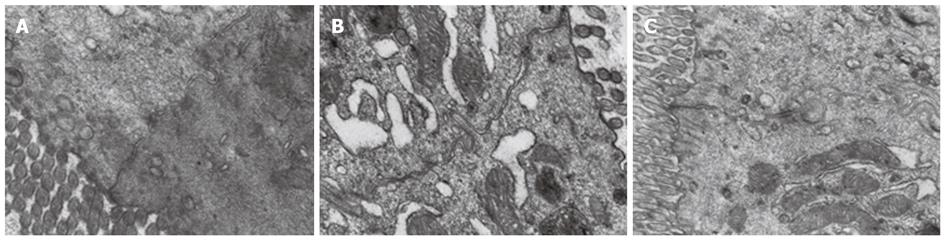
Figure 2 Transmission electron microscopic appearances of diclofenac-induced small intestinal injuries in mice (original magnification × 20 000).
A: Control group; B: Diclofenac group; C: Rebamipide group (400 mg/kg). In the diclofenac group, partial deformation of intestinal epithelial cells, intestinal microvillus reduction, disarrangement of the epithelial surface and broader junctional complexes, tight junction opening were seen. Rebamipide group showed regular and intensive microvillus, and ameliorated tight junction when compared with the diclofenac group.
-
Citation: Diao L, Mei Q, Xu JM, Liu XC, Hu J, Jin J, Yao Q, Chen ML. Rebamipide suppresses diclofenac-induced intestinal permeability
via mitochondrial protection in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(10): 1059-1066 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i10/1059.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1059