Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2012; 18(10): 1048-1058
Published online Mar 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1048
Published online Mar 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1048
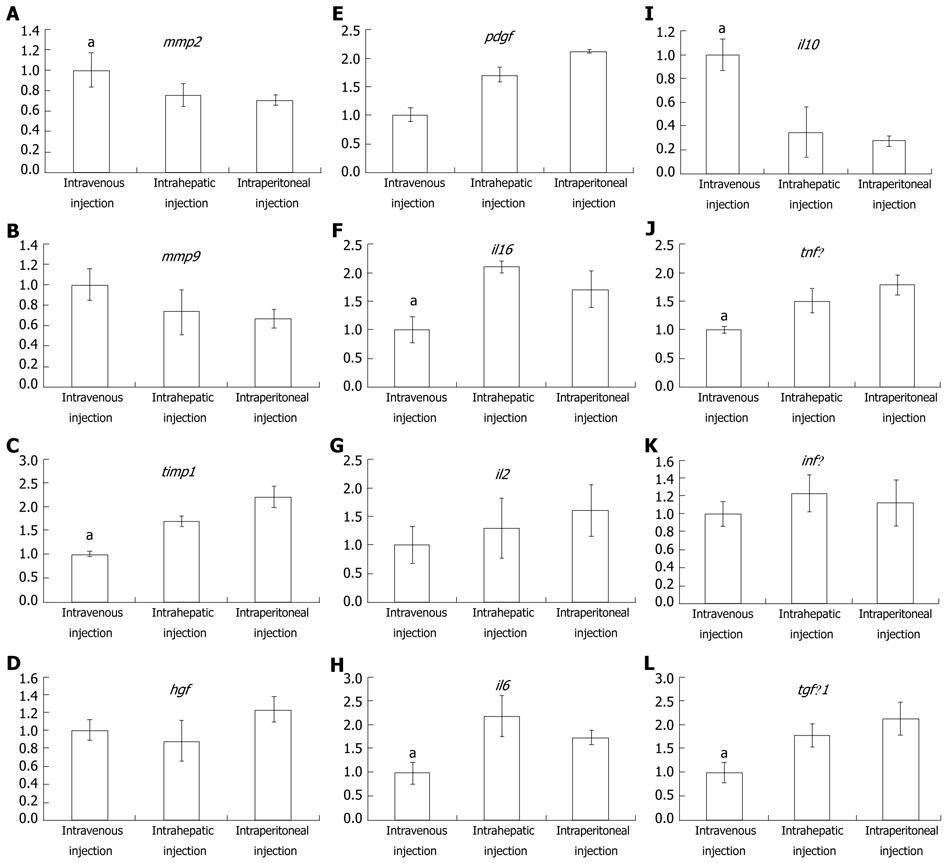
Figure 5 Real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis for detecting the expression difference of cytokines, growth factors and interleukin, which are involved in liver fibrosis progression, among different mesenchymal stem cell transplanted modalities.
The histogram shows the relative expression level for intravenous, intrahepatic and intraperitoneal injections. Data represent the mean ± SE, aP < 0.05. A and I: The expression of mmp2 and il10 in intravenous injection was significantly higher than other injection modalities; F, J, C, H and L: The expression of il1β, tnfα, timp1, il6 and tgfβ1 was significantly lower in intravenous injection than others; E, B, G, K and D: The expression of pdgf, mmp9, il2, hgf, infγ and hgf was not significantly different among the three mesenchymal stem cell injection modalities.
- Citation: Zhao W, Li JJ, Cao DY, Li X, Zhang LY, He Y, Yue SQ, Wang DS, Dou KF. Intravenous injection of mesenchymal stem cells is effective in treating liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(10): 1048-1058
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i10/1048.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1048