Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2011; 17(9): 1143-1151
Published online Mar 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i9.1143
Published online Mar 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i9.1143
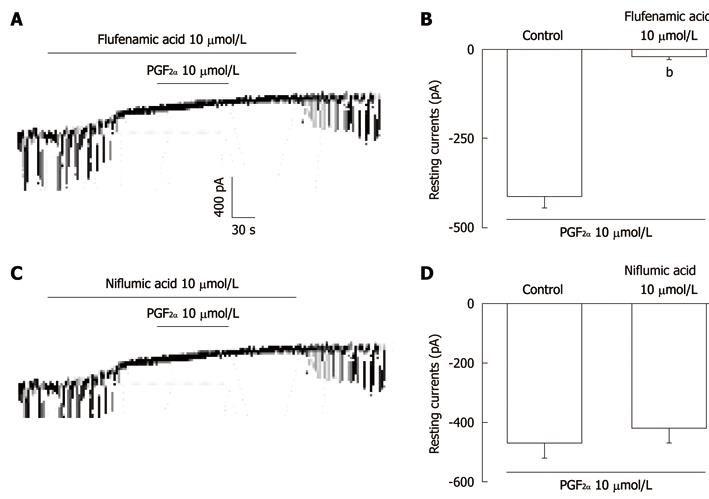
Figure 2 The effects of flufenamic acid or niflumic acid on prostaglandin F2α-induced responses in pacemaker currents in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from mouse small intestine.
A: Application of flufenamic acid (10 μmol/L) abolished the generation of pacemaker currents. Under these conditions, the prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) (10 μmol/L) did not produce tonic inward currents; C: Niflumic acid (10 μmol/L) also abolished the generation of pacemaker currents. However, niflumic acid did not block the PGF2α (10 μmol/L)-induced tonic inward currents. The dotted lines indicate zero current levels. Responses to the PGF2α in the presence of flufenamic acid or niflumic acid are summarized in B and D. Vertical solid line scales denote amplitude of pacemaker current and horizontal solid line scales denote duration of recording (s) pacemaker currents. The bars represent mean ± SE. bP < 0.01 vs the untreated control.
- Citation: Park CG, Kim YD, Kim MY, Koh JW, Jun JY, Yeum CH, So I, Choi S. Effects of prostaglandin F2α on small intestinal interstitial cells of Cajal. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(9): 1143-1151
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i9/1143.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i9.1143