Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2011; 17(6): 750-759
Published online Feb 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.750
Published online Feb 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.750
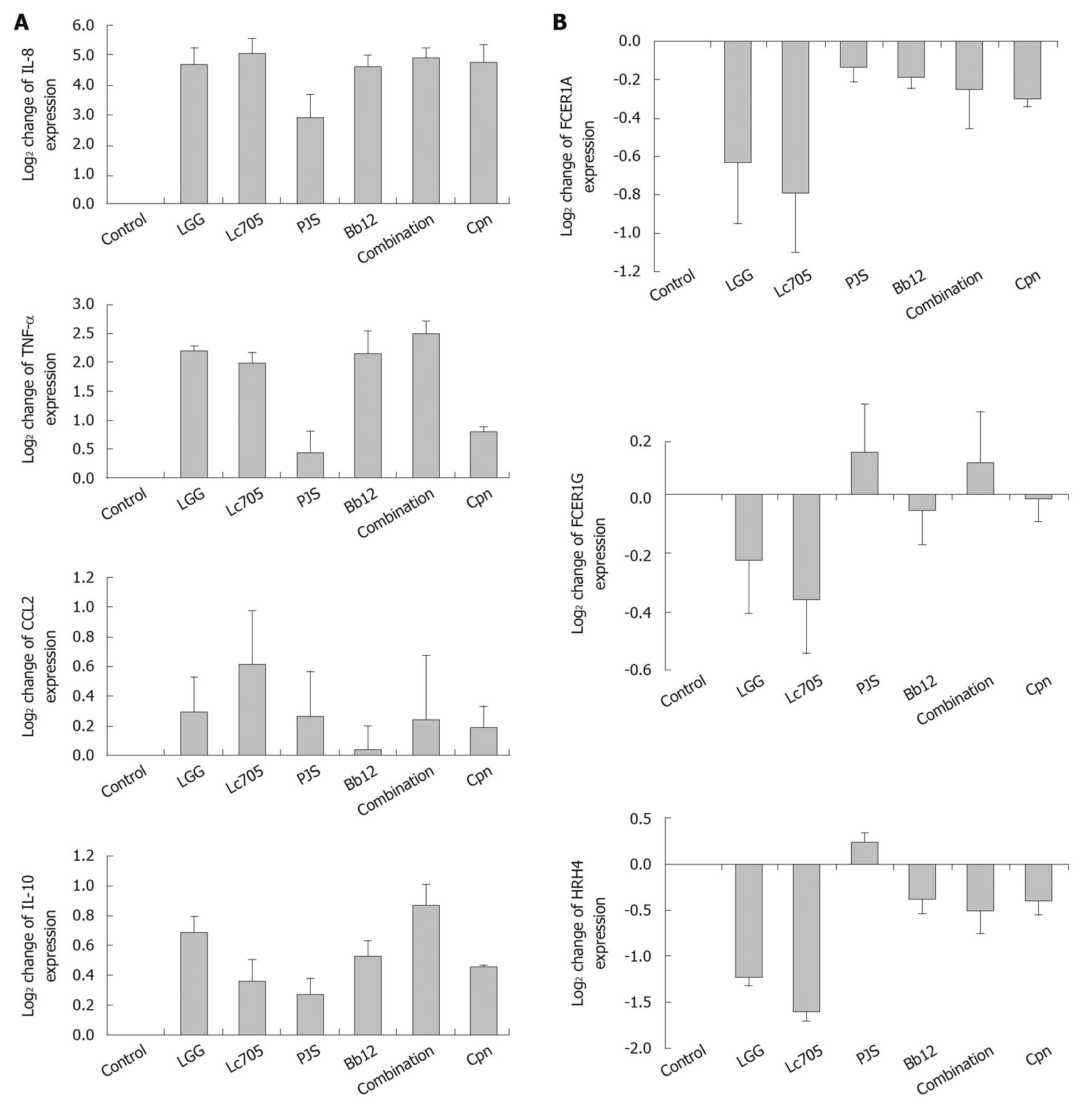
Figure 3 Verification of mast-cell microarray results by quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction with seven selected genes that are involved in mast-cell immune system regulation (A) and mast-cell activation (B).
Gene expression was quantified after 24 h stimulation with four probiotic bacteria; Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG), Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lc705 (Lc705), Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp. shermanii JS (PJS), Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis Bb12 (Bb12) and their combination or with Chlamydia pneumoniae isolate Kajaani 6 (Cpn). Data are mean values ± SE of three independent experiments. IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; CCL2: Chemokine (C-C motif) 2; FCER1A: Fc fragment of IgE high affinity I receptor for α polypeptide; FCER1G: Fc fragment of IgE high affinity I receptor for γ polypeptide; HRH4: Histamine H4 receptor.
-
Citation: Oksaharju A, Kankainen M, Kekkonen RA, Lindstedt KA, Kovanen PT, Korpela R, Miettinen M. Probiotic
Lactobacillus rhamnosus downregulatesFCER1 andHRH4 expression in human mast cells. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(6): 750-759 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i6/750.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.750