Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2011; 17(6): 717-726
Published online Feb 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.717
Published online Feb 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.717
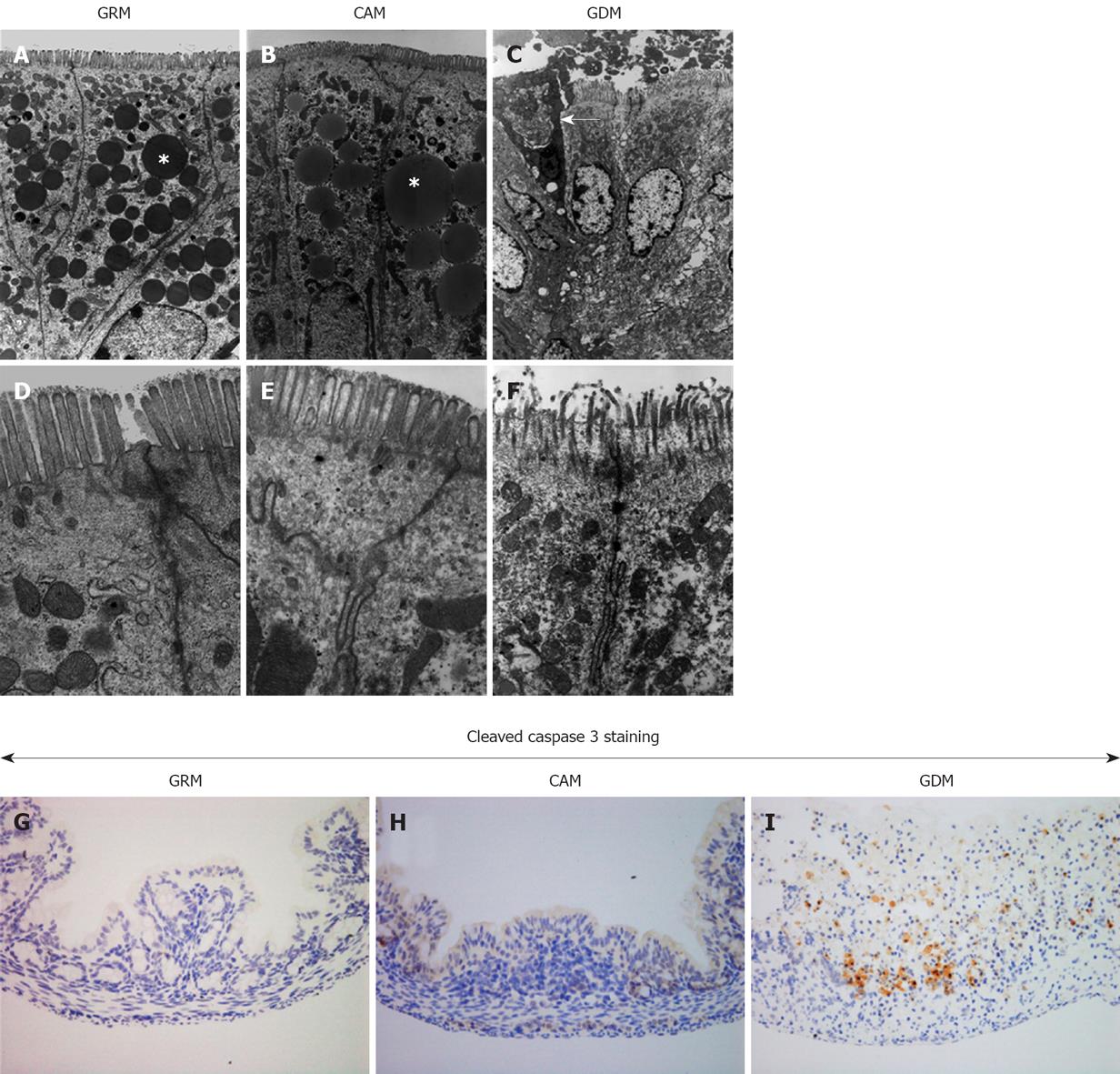
Figure 3 Apoptotic changes observed in the damaged colonic epithelium.
Electron micrographs of colonic epithelia obtained from infant mice with glutamine-rich milk (GRM) (A, D), complete amino acid milk (CAM) (B, E), and glutamine-deleted milk (GDM) (C, F) at low magnification (A-C) and high magnification (D-F). Asterisks (*) represent lipid droplets and the arrow shows an apoptotic cell. G-I: Optical microscopic views (magnification, × 200) of immunohistochemistry for cleaved caspase-3 as a marker of apoptosis using resected tissues from the same mice (G: GRM, H: CAM, I: GDM).
- Citation: Motoki T, Naomoto Y, Hoshiba J, Shirakawa Y, Yamatsuji T, Matsuoka J, Takaoka M, Tomono Y, Fujiwara Y, Tsuchita H, Gunduz M, Nagatsuka H, Tanaka N, Fujiwara T. Glutamine depletion induces murine neonatal melena with increased apoptosis of the intestinal epithelium. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(6): 717-726
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i6/717.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.717