Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2011; 17(47): 5203-5213
Published online Dec 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5203
Published online Dec 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5203
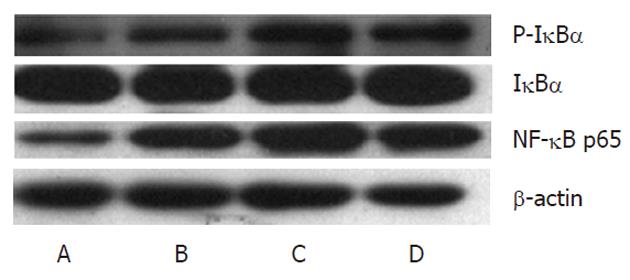
Figure 5 IKK2 inhibitor decreased lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-κB p65 and P-IκBα in livers.
Nuclear levels of the p65 subunit of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) were measured by Western blotting in different groups (A: Control; B: HF group; C: HF + LPS group; D: HF + LPS + IMD group). β-actin was used as a loading control. Administration of IMD at 30 mg/kg doses decreased the DNA binding activity of NF-κB, which was induced by HF and LPS in mice livers. HF: High-fat; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; IMD: IKK2 inhibitor.
- Citation: Wei J, Shi M, Wu WQ, Xu H, Wang T, Wang N, Ma JL, Wang YG. IκB kinase-beta inhibitor attenuates hepatic fibrosis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(47): 5203-5213
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i47/5203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5203