Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2011; 17(47): 5203-5213
Published online Dec 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5203
Published online Dec 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5203
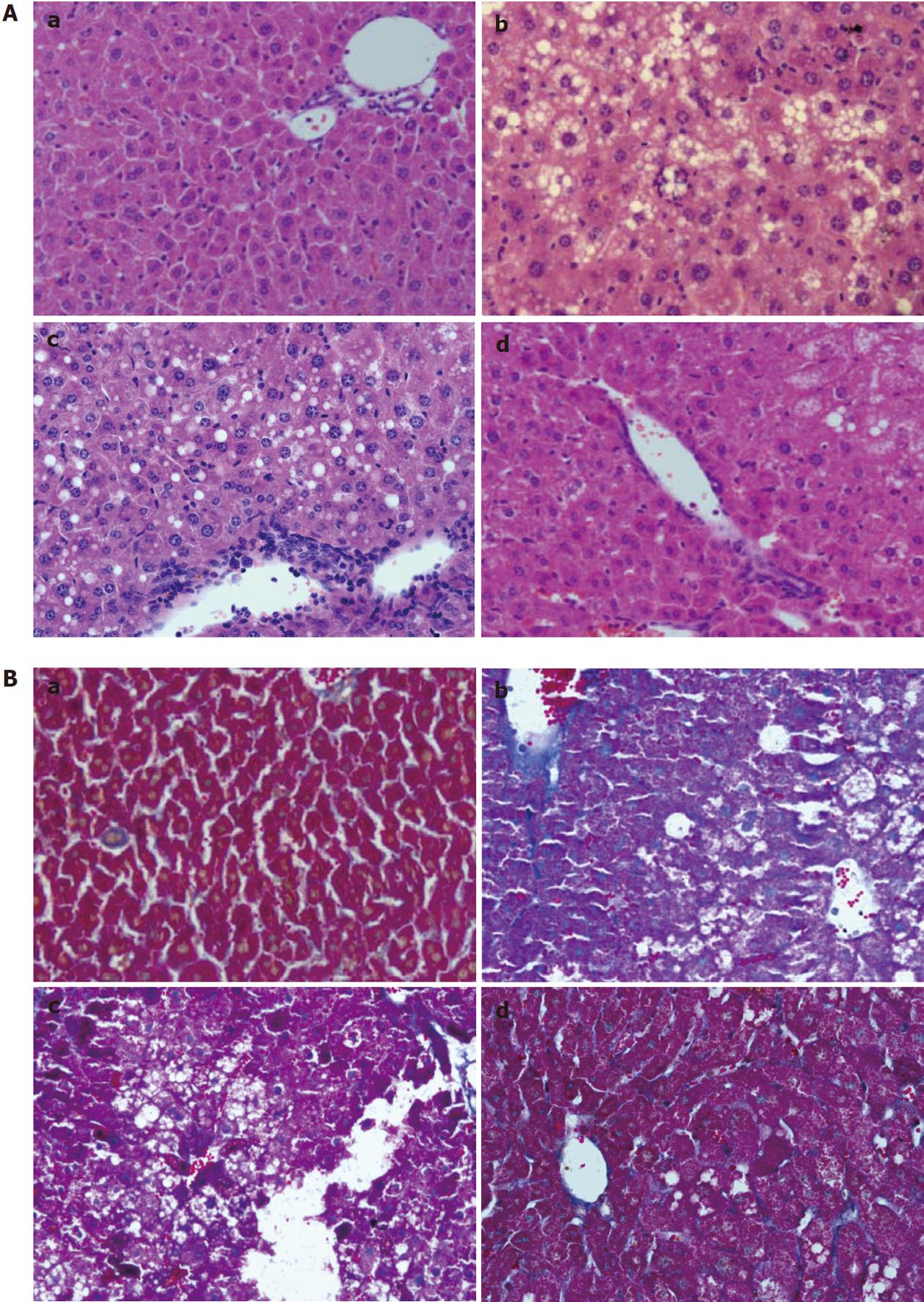
Figure 2 Hematoxylin and eosin stain and Masson staining in sections of (a) control group; (b) HF group; (c) HF + LPS group; and (d) HF + LPS + IMD group.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin stain. Macrovesicular steatosis, lobular inflammation and balloon degeneration of hepatocytes were observed in liver sections of HF-treated mice and HF + LPS + treated mice with a significantly large amount of inflammatory cell infiltration surrounding the centrilobular veins of the liver. Significant amelioration was observed in the group treated with IMD (d); B: Masson staining. A thin lining of collagen was observed in the HF group, HF + LPS group and HF + LPS + IMD group. With LPS treatment, there was an increase in the amount of collagen accumulated along the central vein with the presence of collagen in the pericellular area. Treatment with IMD reduced LPS-induced collagen accumulation. HF: High-fat; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; IMD: IKK2 inhibitor.
- Citation: Wei J, Shi M, Wu WQ, Xu H, Wang T, Wang N, Ma JL, Wang YG. IκB kinase-beta inhibitor attenuates hepatic fibrosis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(47): 5203-5213
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i47/5203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5203