Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2011; 17(44): 4890-4898
Published online Nov 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4890
Published online Nov 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4890
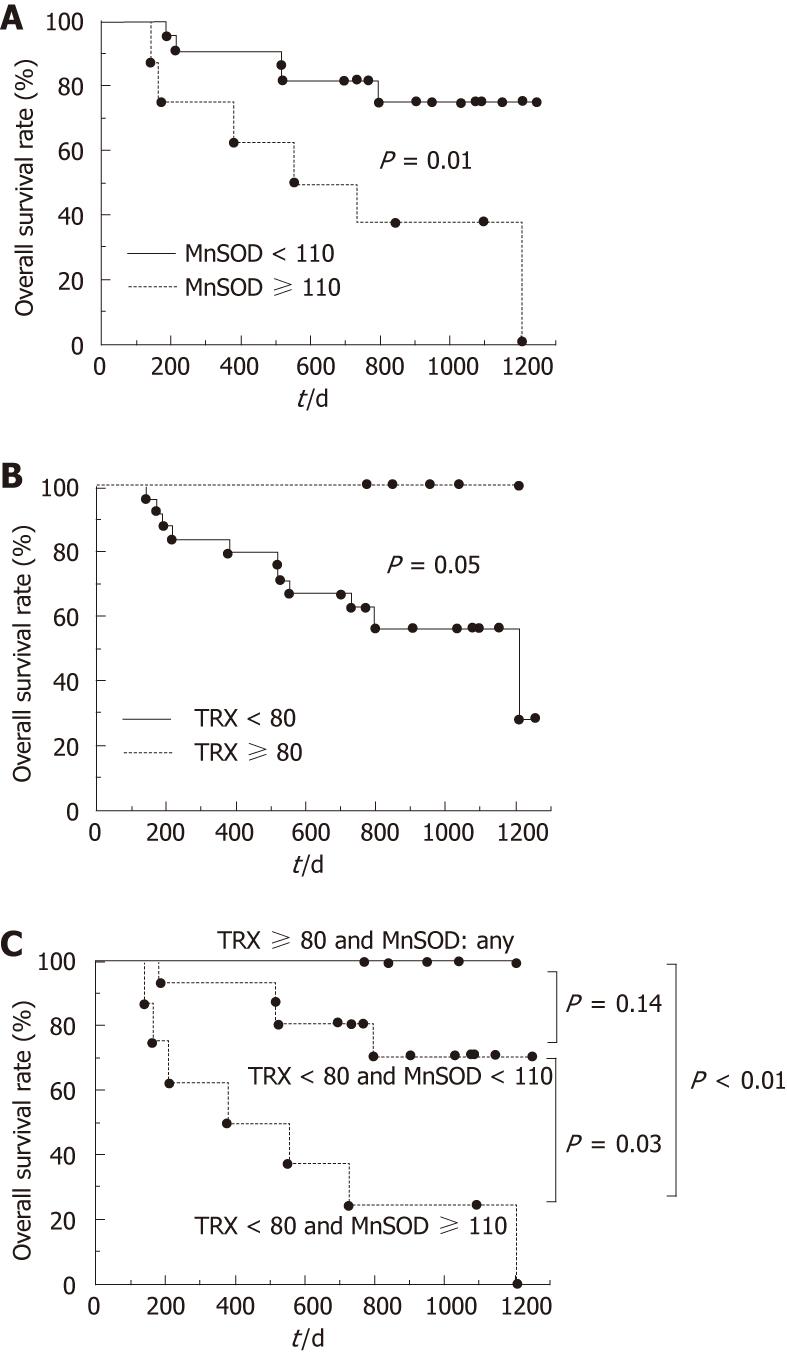
Figure 3 Overall hepatocellular carcinoma patient survival based on serum levels of manganese superoxide dismutase or thioredoxin.
Overall survival was plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method after separation into two or three groups defined as follows: A: Manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) < 110 ng/mL or ≥ 110 ng/mL; B: Thioredoxin (TRX) < 80 ng/mL or ≥ 80 ng/mL; TRX ≥ 80 ng/mL, TRX < 80 ng/mL; C: MnSOD < 110 ng/mL, or TRX < 80 ng/mL and MnSOD ≥ 110 ng/mL. The overall survival rate was lower in patients with MnSOD levels ≥ 110 ng/mL (P = 0.01) (A). Also, cumulative patient survival rate tended to be lower in patients with TRX levels < 80 ng/mL (P = 0.05) (B). Among these groups, patients with serum TRX levels < 80 ng/mL and serum MnSOD levels ≥ 110 ng/mL had the poorest prognosis (C).
- Citation: Tamai T, Uto H, Takami Y, Oda K, Saishoji A, Hashiguchi M, Kumagai K, Kure T, Mawatari S, Moriuchi A, Oketani M, Ido A, Tsubouchi H. Serum manganese superoxide dismutase and thioredoxin are potential prognostic markers for hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(44): 4890-4898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i44/4890.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4890