Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2011; 17(44): 4890-4898
Published online Nov 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4890
Published online Nov 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4890
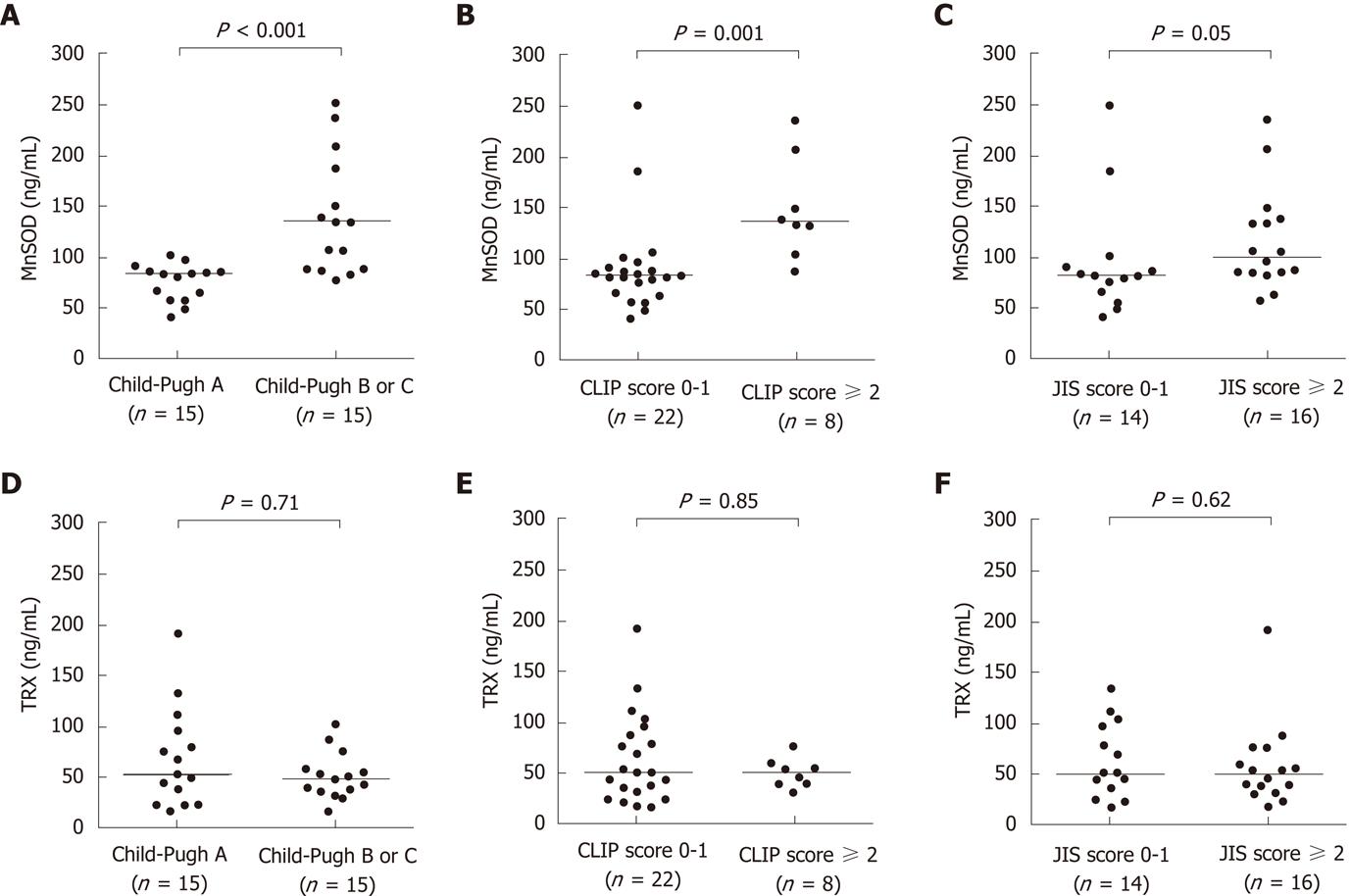
Figure 2 Clinical significance of serum manganese superoxide dismutase and thioredoxin levels in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In the hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) group, differences in serum manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) and thioredoxin (TRX) levels were evaluated based on Child-Pugh stage, cancer of the liver italian program (CLIP) score and Japan integrated staging (JIS) score. A: Serum MnSOD levels were significantly higher in patients with Child-Pugh B or C compared to those with Child-Pugh A (P < 0.001); B: Serum MnSOD levels in patients with a CLIP score of 2 or greater were significantly higher compared to levels in patients with a CLIP score of 0 or 1 (P = 0.001); C: In addition, serum MnSOD levels tended to be higher in patients with a JIS score of 2 or greater compared to patients with a JIS score of 0 or 1 (P = 0.05); D-F: In contrast, serum TRX levels were not significantly different based on Child-Pugh stage, CLIP score or JIS score.
- Citation: Tamai T, Uto H, Takami Y, Oda K, Saishoji A, Hashiguchi M, Kumagai K, Kure T, Mawatari S, Moriuchi A, Oketani M, Ido A, Tsubouchi H. Serum manganese superoxide dismutase and thioredoxin are potential prognostic markers for hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(44): 4890-4898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i44/4890.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4890