Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2011; 17(43): 4772-4778
Published online Nov 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4772
Published online Nov 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4772
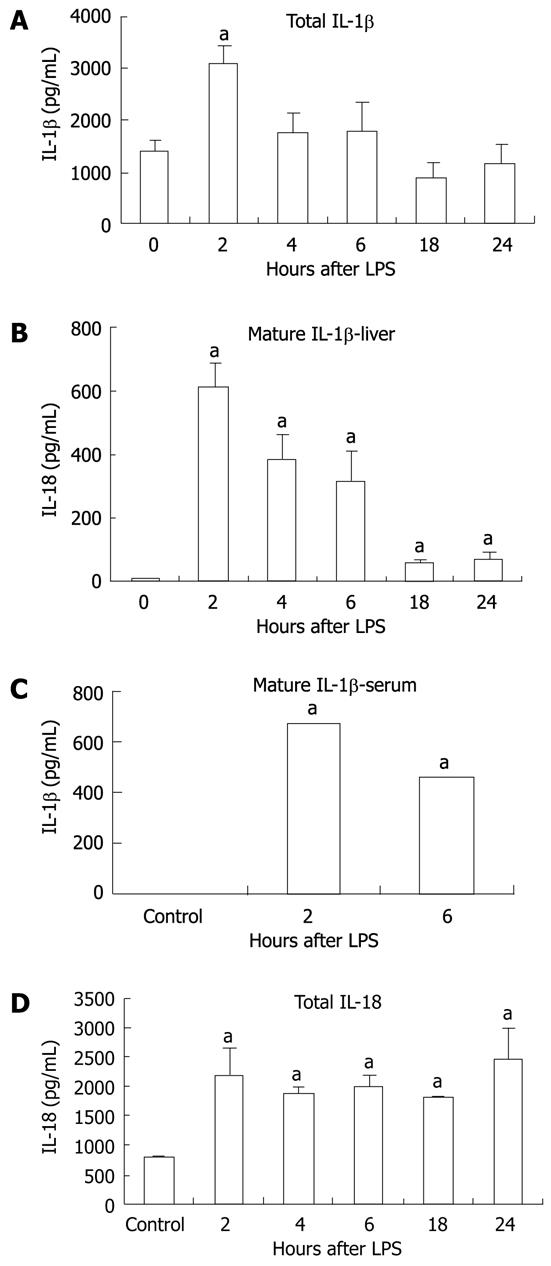
Figure 5 Lipopolysaccharide increased interleukin-1β and interleukin-18 protein.
Protein level was detected in liver tissue by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for total-interleukin (IL)-1β (pro-IL-1β and cleaved IL-1β) (A), cleaved IL-1β in the liver tissue (B),cleaved IL-1β in the serum (C) and total IL-18 (pro-IL-18 and cleaved IL-18) (D) in liver tissue. The values shown are the fold change compared to non-Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulated control. Protein levels were normalized to total protein concentrations in each tissue sample. Mean ± SD are shown. n = 3 per group (except at 2 h LPS stimulation, where n = 2 due to an outlier), aP < 0.01.
- Citation: Ganz M, Csak T, Nath B, Szabo G. Lipopolysaccharide induces and activates the Nalp3 inflammasome in the liver. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(43): 4772-4778
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i43/4772.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4772