Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2011; 17(41): 4563-4571
Published online Nov 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i41.4563
Published online Nov 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i41.4563
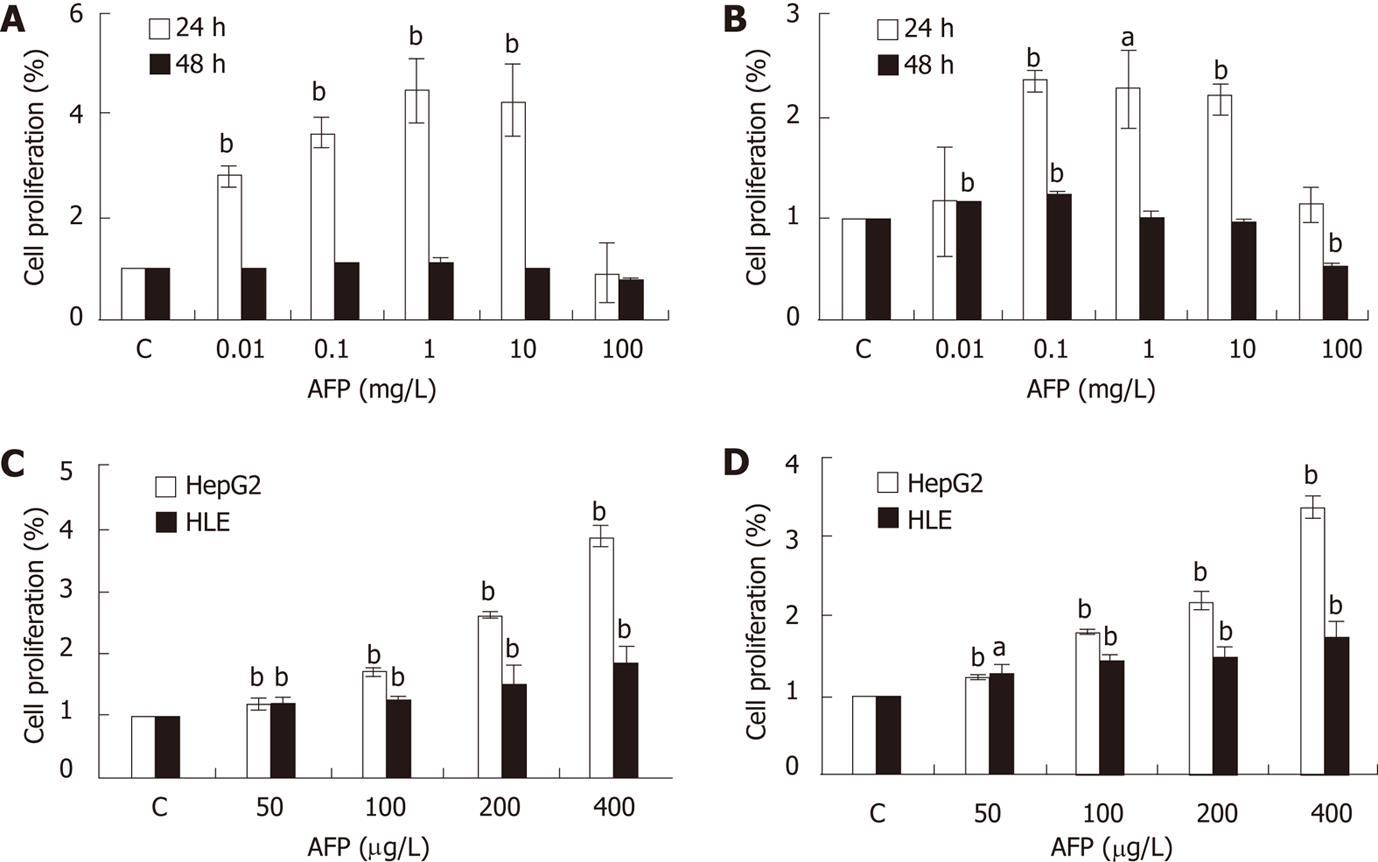
Figure 3 Effects of alpha fetoprotein in proliferation of HepG2 and HLE cells.
Different concentrations (0, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10 and 100 mg/L) of alpha fetoprotein (AFP) were tested in cell culture. The proliferation of HepG2 (A) and HLE (B) cells was evaluated with the dimethylthiahzolyl-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay at 24 and 48 h. HepG2 and HLE cells were further tested with 0, 50, 100, 200 and 400 μg/L AFP and proliferation was evaluated by MTT (C) and a cell counting kit (cck)-8 assay (D) at 24 h. The differences in proliferation between HepG2 and HLE cells were statistically analyzed with SPSS16 software. Data are representative of experiments that were repeated three times and are presented as mean ± SD for 6-9 samples.
- Citation: Li P, Wang SS, Liu H, Li N, McNutt MA, Li G, Ding HG. Elevated serum alpha fetoprotein levels promote pathological progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(41): 4563-4571
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i41/4563.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i41.4563