Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2011; 17(4): 526-533
Published online Jan 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.526
Published online Jan 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.526
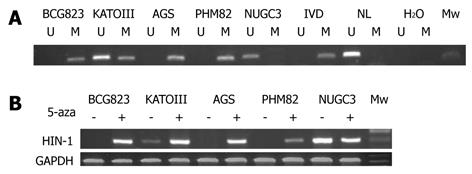
Figure 1 Silence of high in normal-1 gene expression due to methylation of high in normal-1 gene promoter in gastric carcinoma cell lines.
A: Methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction analysis of high in normal-1 (HIN-1) gene promoter methylation in five gastric carcinoma cell lines. U: Unmethylated alleles; M: Methylated alleles. In vitro methylated DNA (IVD) and DNA from normal human peripheral lymphocytes were used as methylated and unmethylated controls; B: Gastric cancer cell lines were treated with or without 5-aza-CdR (-AZ) for up to 96 h. HIN-1 mRNA levels were measured by semi-quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) served as control. The 1-kb marker indicated an appropriate size for the amplified products. HIN-1 expression varied among cell lines. The presence of methylation of HIN-1 corresponds directly to the loss of expression of the genes in each cell line.
- Citation: Gong Y, Guo MZ, Ye ZJ, Zhang XL, Zhao YL, Yang YS. Silence of HIN-1 expression through methylation of its gene promoter in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(4): 526-533
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i4/526.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.526