Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2011; 17(4): 470-477
Published online Jan 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.470
Published online Jan 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.470
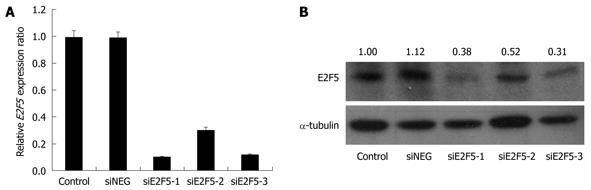
Figure 3 Small interfering RNA-mediated silencing of E2F5 gene expression in HepG2 cells.
A: After siE2F5 transfection into the HepG2 cells, E2F5 expression was measured by real time quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. Human GAPDH gene was used as an internal control. The X axis represents samples and the Y axis relative E2F5 expression ratios (siE2F5 or siNEG/control); B: E2F5 expression in Western blotting analysis was measured by densitometry. Alpha-tubulin was used as an internal control. E2F5 specific signal intensities of siE2F5-treated cells are profoundly repressed compared with siNEG-treated cells. Control: HepG2 cells without transfection; siNEG: Negative oligonucleotide (siNEG) transfected HepG2.
- Citation: Jiang Y, Yim SH, Xu HD, Jung SH, Yang SY, Hu HJ, Jung CK, Chung YJ. A potential oncogenic role of the commonly observed E2F5 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(4): 470-477
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i4/470.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.470