Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2011; 17(4): 459-469
Published online Jan 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459
Published online Jan 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459
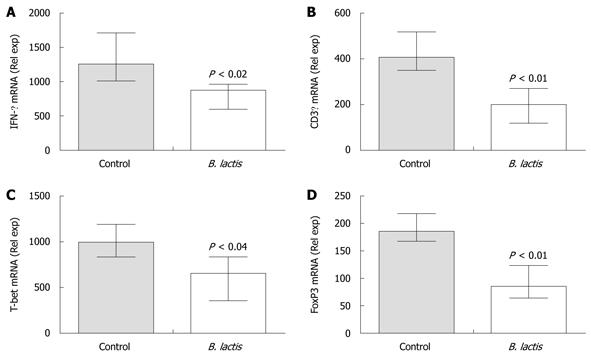
Figure 6 Bifidobacterium lactis feeding significantly diminished mRNA expression of Th1 cell markers and significantly increased mRNA expression of a Treg marker in colon of recipient mice following adoptive T cell transfer.
The expressions of mRNA coding for interferon-γ (IFN-γ) (A), CD3γ (B), T-bet (C) and FoxP3 (D) were assessed in colon samples of recipient mice by real-time polymerase chain reaction using the low density array technology. Results are expressed as the mean ± interquartile-range (n = 5 mice per group) and statistical significance is indicated. B. lactis: Bifidobacterium lactis.
-
Citation: Philippe D, Favre L, Foata F, Adolfsson O, Perruisseau-Carrier G, Vidal K, Reuteler G, Dayer-Schneider J, Mueller C, Blum S.
Bifidobacterium lactis attenuates onset of inflammation in a murine model of colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(4): 459-469 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i4/459.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459