Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2011; 17(4): 459-469
Published online Jan 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459
Published online Jan 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459
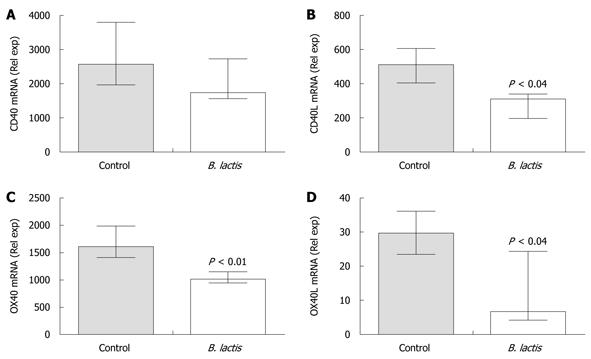
Figure 5 Bifidobacterium lactis feeding diminished the expression of mRNA coding for antigen-presenting cells and T cell costimulatory molecules in colon of recipient mice following adoptive T cell transfer.
The expressions of mRNA coding for CD40 (A), CD40 ligand (CD40L) (B), OX40 (C) and OX40 ligand (OX40L) (D) were assessed in colon samples of colitic and healthy mice by real-time polymerase chain reaction using the low density array technology. Results are expressed as the mean ± interquartile-range (n = 5 mice per group) and statistical significance is indicated. B. lactis: Bifidobacterium lactis.
-
Citation: Philippe D, Favre L, Foata F, Adolfsson O, Perruisseau-Carrier G, Vidal K, Reuteler G, Dayer-Schneider J, Mueller C, Blum S.
Bifidobacterium lactis attenuates onset of inflammation in a murine model of colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(4): 459-469 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i4/459.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459